- 1. What is a bottleneck in a business process and how to solve it
What is a bottleneck in a business process and how to solve it
Bottlenecks in business process are the great enemy of effectiveness, but there are steps to take to prevent them and boost your organization’s efficiency without obstacles.
In the following article, we will detail what a bottleneck is, along with keys to identifying it, examples, and tips that will take your company to the next level.
Additionally, we will explore the functionalities that Qflow BPM offers to recognize, avoid, and resolve bottleneck in business process, providing advice to streamline your business process management.
What are bottlenecks in business process?
A bottleneck in a company is the point where tasks begin to accumulate, hindering the usual production pace and even interrupting operations in severe cases.
Bottlenecks occur when a high volume of tasks exceeds the response capacity of the organization’s collaborators. Without attention, a bottleneck prevents the process from continuing, exacerbating employee workload and service delays, resulting in a loss of competitiveness and a decline in customer satisfaction.
What are the most common causes of their appearance?
Bottlenecks in business processes arise from different triggering causes:
- Process demand increases beyond expectations, exceeding the response capacity of the assigned collaborators. For example, if higher attention to leave request processes is not foreseen during peak vacation seasons, such as summer or popular holidays, they may be affected by a bottleneck due to the increase in employees interested in scheduling time off simultaneously.
- Lack of automation in process management. An organization that continues to manage its processes manually is more vulnerable to bottlenecks, as it lacks standardization and control that allows monitoring each process promptly and effectively.
- Design flaws. In this scenario, the process configuration has flaws that affect its effectiveness, making it unfeasible regardless of the quality of its management.
- Suboptimal management. For example, task responses may have been assigned to a low-performing user. Without appropriate time control measures and task reassignment, a user’s inefficiency can trigger a bottleneck.
Why is it crucial to identify them?
Knowing the signs indicating the presence of a bottleneck in your business processes is essential to prevent them or, failing that, to resolve them quickly. But why?
Speed is a great ally in eliminating bottlenecks because the longer they remain unattended, the greater the consequences for the organization’s productivity. Considering the interconnected nature of the business processes that make up a modern organization’s activity, if a bottleneck is not resolved promptly, it can generate new delays or interruptions in linked processes.
Other consequences of neglecting bottlenecks are:
- Poor quality in task responses. In cases of urgency facing a bottleneck, a user may receive a higher volume of tasks in less time to unclog the backlog of unattended actions. If a user has to respond to more tasks more quickly to resolve the bottleneck, their responses may lose quality, affecting process standardization.
- Delays occur. If a user fails to respond to their tasks on time, causing a bottleneck, their delay impacts the response times of other collaborators. Systematic delays in task responses from a process consequently lead to a delay in the resolution of the entire process, which can affect customers, suppliers, and the organization as a whole.
- Productivity decreases. Similarly, the interruption in the process flow prevents collaborators assigned to tasks after the bottleneck from having actions to execute for the total duration of the problem.
- Customer and supplier satisfaction decreases. Delays in process management damage the relationship of customers and suppliers with the organization, reducing their satisfaction with the business agreement and potentially disrupting it.
- Credibility is lost. A company that fails to meet stipulated deadlines due to neglecting its bottlenecks loses credibility in the market.
- Competitiveness declines. If a company loses credibility in its sector, its ability to stand out against the competition is greatly reduced, interrupting its growth.
- Customer volume decreases. As a consequence of the previously detailed factors, existing customers may decide to terminate their contracts with the company, while new customers will not be attracted to the proposal.
How to identify them?
Knowing the consequences of neglecting bottlenecks, it is essential to learn how to identify them to design optimal prevention and management plans.
The best way to resolve bottlenecks in business processes is to decompress them before they generate significant delays. Learning how to do it and executing it effectively takes time and attention, but implementing a systematic control designed for the organization’s reality reduces dedication.
To start, there are two key signs of the presence of a bottleneck in process management:
- When a process takes too long in a task. If the process resolution takes longer than stipulated, it is necessary to analyze in which step the delay occurred, thus revealing the cause of the bottleneck. This requires a deep understanding of the organization’s processes: a process is only as strong as its initial mapping. Identifying the roles, data, and actions that compose them, the times involved, and the actors involved (collaborators, customers, suppliers, etc.) facilitate the early identification of delays and bottlenecks.
- If a team or user consistently has an overload, it may mean that a bottleneck is affecting the normal distribution of work. Fluid communication with collaborators is essential for the organization’s efficiency.
How to prevent them?
Time control by stages
This functionality offered by Qflow allows monitoring of the time required for a task or sequence of tasks within a project. By knowing the stipulated times, any variation alerts the possibility of a bottleneck.
Iterations and frequent updates
To avoid errors in the design of processes that subsequently generate bottlenecks, it is important to make the necessary iterations before implementation. The key is to test the process to see what works well before using it and periodically during its use; incorporating relevant updates to adapt it to new needs that may arise.
Listening to collaborators
Having an open-door policy to listen to and address complaints directly. Using tools like employee well-being surveys, talking to team leaders to see if there is enough staff for the assigned tasks, and quickly detecting overload.
Data analysis
The most efficient way to control a process is by analyzing data. Therefore, it is important to conduct periodic audits. Qflow’s 100% auditable feature generates records for each action taken, greatly facilitating audits.
Additionally, Qflow Task, Qflow’s tool that allows initiating processes, responding to tasks, and monitoring information; offers customizable control panels with user-friendly indicators to alert against delays and setbacks. For example, through a traffic light indicator, the user instantly detects delays in the expected time for responding to a task.
Example of bottlenecks in business process
Let’s take a purchase request process as an example, designed, automated, and monitored through a BPM software like Qflow.
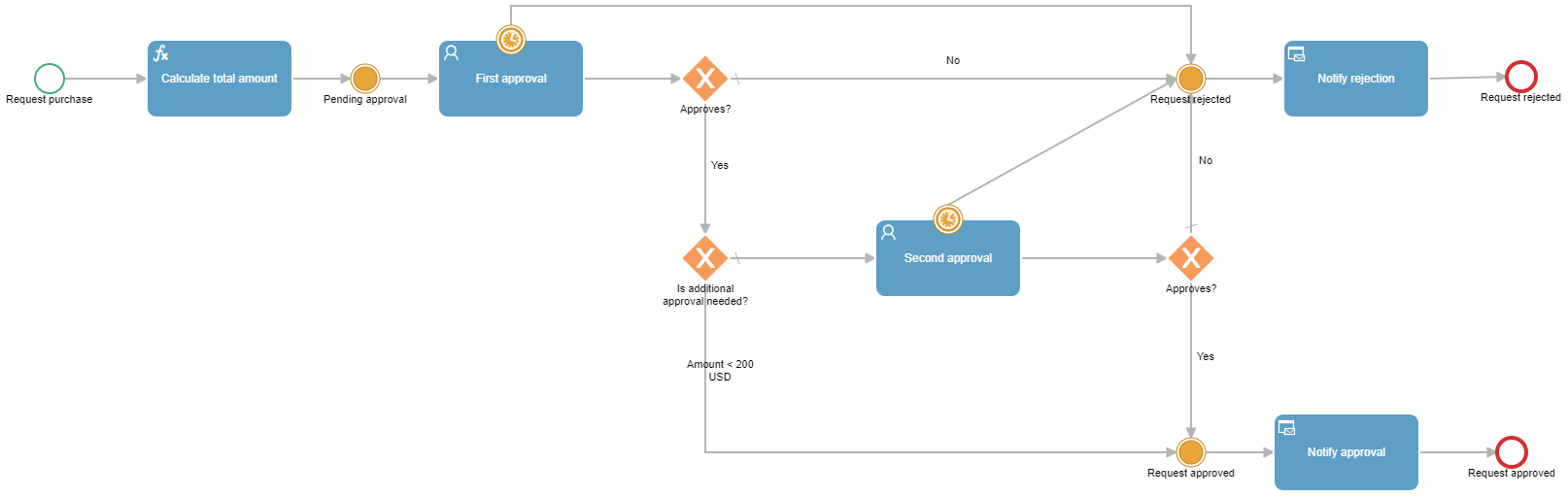
In its gallery of pre-designed and fully customizable templates, Qflow offers the ready-to-use purchase request template, which includes the following steps:
- Purchase request. Initiates the process by submitting a form with the necessary data for action, such as the reason for the purchase, total cost, and area that requires it.
- First approval. Once the information is received, a task is sent to the “first reviewer” role, responsible for approving or rejecting the purchase request. The assigned user must enter the form, verify the presented information, and make a decision.
- Second approval. In cases where the total purchase amount exceeds a limit established in the process design, the request will require a second approval to proceed. This task is assigned to a higher-ranking user, with the necessary authority to approve the expense.
- Final notification. Finally, the process initiator receives a notification in their email communicating the resolution, whether it’s the approval of the purchase or its rejection, along with relevant comments.
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario of a substantial increase in purchase requests, for example, due to a previously scheduled office supplies replenishment.
In this case, Qflow’s purchase request template prevents bottlenecks by configuring time controls on approval tasks. This includes sending a reminder 10 days after the task is assigned, alerts at 20 days, and automatic task expiration after one month. The times, as well as every element of the template, are fully customizable to the process needs.
Furthermore, to prevent employee workload overload, Qflow offers a series of automatic task assignment rules aimed at intelligent and equitable distribution of actions for each process.
For instance, the rule of assigning tasks to the user with fewer tasks can be applied to the “first reviewer” role, assigning the first approval of the purchase request to the collaborator with fewer pending actions within the purchasing department. In scenarios that warrant it, Qflow allows for even more specificity with the rule of assigning tasks to the user with fewer tasks in the process template, considering only pending actions in purchase request processes to select the ideal user.
Additionally, in version 5.4, Qflow introduced the new sequential distribution rule (Round Robin), enabling sequential and cyclical distribution of tasks among role members. In the case of the second approval, the Fair Distribution rule could be applied to the “second approver” role so that each secondary evaluation of a purchase request falls on a different manager, thus avoiding workload overload even among high-level executives of the organization.
Conclusion
Bottleneck in business process represent a significant obstacle between your organization and efficiency, but thanks to Qflow, concerns about delays and setbacks in your processes can be a thing of the past.
Effective management of business processes is vital to compete in today’s dynamic business environment. To preserve efficiency and prevent your company’s productivity from being affected by bottlenecks, Qflow allows you to identify, prevent, and resolve these issues while optimizing resources and maintaining a high level of satisfaction among customers, suppliers, and employees.
With a wide range of features available to recognize bottlenecks at early stages, resolve them in record time, and even prevent their occurrence, Qflow will transform your company’s business process management by incorporating tools such as stage-based time control, automatic task delegation, and customizable control panels, facilitating data analysis and evidence-based decision-making.
With Qflow, optimize your processes and maximize your company’s performance. Don’t wait for bottlenecks to affect your business process management. Try Qflow now and take your company to its maximum potential!