Introduction
In the whirlwind of today’s business world, Business Process Management (BPM) emerges as an optimal solution to ensure the efficiency of your operations. But what is it, and how is BPM implemented? In this article, we will explore the meaning of BPM and the different types of business processes, answering the most frequently asked questions about BPM.
What is BPM?
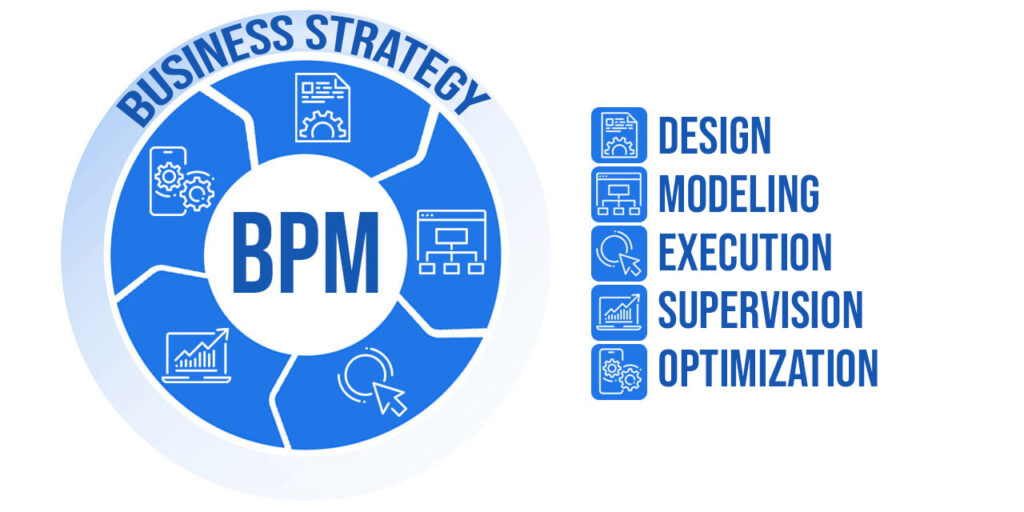
Business Process Management, or BPM by its acronym in English (Business Process Management), is a methodology that designs, automates, monitors, and analyzes the business processes of an organization systematically.
The goal of BPM is to model and improve business processes, optimizing their performance to enhance the success of the company.
What is a business process?
One of the main questions about BPM is how to identify a business process. A business process is any set of activities that an organization performs with the established goal of addressing a specific problem or demand in its operations.
The functioning of every company relies on the efficiency of its processes, both for customer satisfaction and for the performance of its employees.
There are different types of processes, classified based on their importance and the users who interact with them:
- Essential processes are those that condition the primary activity of a company. For example, the process of selling products in a company dedicated to merchandise marketing.
- Support processes are those that support operations, ensuring the resources and infrastructure necessary for the organization’s operations. While each company determines its support processes, there is a certain standardization in the activities they comprise, highlighting processes such as Human Resources management, technical support, and accounting.
- Administrative processes are those that monitor and control other processes, measure the organization’s performance, and ensure the enhancement of its operations. These processes can be executed prior to, simultaneously with, or after essential and support processes. For example, setting annual goals for an organization or conducting employee performance evaluations.
What are the types of BPM?
Similarly, BPM types are categorized according to their function, resulting in three main categories:
- Document-centric BPM, the tool for optimizing document management within an organization. Its goal is to centralize documents in one place, replacing the exchange of materials via email and organizing their creation, review, signing, and storage systematically.
- Human-centric BPM revolves around the intervention of one or more employees, usually requiring their approval to execute. In these cases, functionalities such as role definition, automatic assignments, and alerts play a significant role.
- Integration-centric BPM connects the chosen BPM solution with other tools used by the company. Unlike Human-centric BPM, integrations require little or no intervention from employees, increasing productivity by automating data exchange and storage between the software in use.
What benefits does using a BPM tool bring?
There are countless advantages in process management with BPM software. With the aim of boosting the efficiency and performance of an organization, implementing a BPM tool can also:
- Reduce process execution times
- Increase customer and employee satisfaction
- Facilitate audits within the organization
- Simplify adherence to international regulations and standards
- Improve decision-making through orderly and equitable access to information
- Drive goal achievement through more efficient planning
- Reduce costs related to errors and delays in operations
- Promote innovation through process monitoring and iteration
What requirements must my organization meet to implement a BPM tool?
As we addressed in the article Innovation in process management: Innovation in process management: implementing Qflow Cloud in your organization, there are certain requirements that an organization must ensure before incorporating a BPM tool.
The primary decisive factor is the organization’s maturity level, meaning the degree of process management development within the company. To model, automate, and optimize a business process, it must be replicable, repeatable, and documented. Once the organization reaches an optimal level of maturity, successful implementation of a BPM tool is guaranteed.
Other requirements include having the necessary personnel and time to train on and work with the tool, selecting the appropriate licensing model for the tool and acquiring it, and of course, selecting the right tool.
How do I choose the ideal BPM tool for my organization?
Once you have answered all your questions about BPM and its uses, you may start researching tools to find the best fit for your company. BPM tools abound in the current market, offering a range of options for each organization to find the ideal solution for its processes. To do this, the company must have the time to conduct a survey of available options, testing the tools through free trials, and weighing the available functionalities against the organization’s requirements.
If your organization requires a flexible and highly customizable tool, Qflow offers the versatility needed to adapt to each company’s operating style. Additionally, our constant updates reaffirm our commitment to innovation, adapting to your needs as they arise. Take advantage of our comprehensive training and technical support, preparing your team of employees to take the organization to the next level with Qflow.
Conclusion
Business Process Management or BPM is a powerful tool for driving your organization’s operations. By modeling, automating, and optimizing your processes with BPM, your customers and employees enjoy seamless operations, and the organization finds the flexibility needed to embrace innovation and position itself against the competition.
Now that you found answers to the main questions about BPM, explore Qflow and discover the advantages of enhancing your business processes with our BPM tool.