Introduction
Quality management is a fundamental discipline for any company that aims to deliver high-quality products or services to its customers. However, quality management can be a complex process, and that’s where Business Process Management (BPM) software turns into a very useful tool for implementing a quality management system and easily and quickly certifying it in ISO 9001. This automation of key processes improves efficiency and effectiveness.
In this article, we will explore two examples of how to use BPM software to automate the management of documents and actions related to your Quality Management System (QMS).
Creation, review, and approval of quality management system documents
Documentation is an integral part of the quality management system that ensures consistency in processes and procedures. In the article Essential documentation in a Quality Management System: Keys to compliance you can find a complete guide on the subject.
However, the creation, review, and approval of these documents, a key process in a QMS, can be labor-intensive and error-prone.
Automating this process with BPM software can help companies to:
- Standardize and organize the process of creating, reviewing, and approving new documents.
- Reduce the time and effort required for document management.
- Facilitate tracking the status of documents and individuals responsible for each task.
- Streamline communication among involved users.
- Conduct audits of decisions made.
- Maintain workflow continuity even when a person is absent.
- Control timelines with reminders, alerts, and deadlines.
- Easily notify and disseminate newly approved documents.
Ready-to-use document approval template
Qflow offers a ready-to-use “Document approval” template that can be adapted to the document approval process of any organization, regardless of its size.
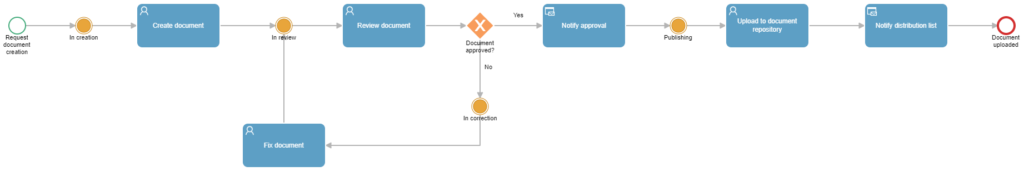
Tasks in this process include:
Document creation request
In this initial step, basic document information such as the title, version, and description is entered.
Simultaneously, those responsible for creating and reviewing documents are defined, who can be individuals or fixed groups of people, or anyone belonging to a work queue capable of handling this task.
Additionally, the distribution list to be notified of the existence of a new quality document upon approval is also established.
Document creation
It is the task received by the user defined as the Document Creator, in which they can see the information entered in the previous step and must upload the requested document as an attachment to the process for it to be sent for review.
The only possible response for this task is “Submit for Review.”
Document review
It is the task received by the user defined as the Document Reviewer, in which they can see the information entered in the previous steps and must download the attached file to carry out the corresponding review.
Possible responses to this task are “Approve” if there are no objections to the document, or “Correct” if changes are required. In the latter case, the Reviewer must enter the requested changes in a comments field in the process to guide the Document Creator, who will receive the task “Correct Document.” The Document Creator must then make the requested changes, upload the new version of the document, and submit it for review again.
Document repository upload
In this template, this task is a user task, involving the manual uploading of the document to a document repository. It can be deleted if your organization does not have a document repository or if you want the documents to be hosted only in Qflow. In the latter case, you have the option to easily configure views in Qflow that allow you to access all approved documentation with the metadata that is most important to you, in an organized and straightforward manner.
If you wish for greater automation, you can replace this task with a service task to perform integration, for example, with SharePoint, and automatically upload documents once approved, without requiring user intervention.
Notification steps
In this template, two automatic notification steps are defined: the first is to notify the Document Creator when the document is approved, and the second is to notify the distribution list defined in the initial step that a new document has been published.
It is not necessary to be within the tool to view notifications; they can be received via email or on mobile devices for even smoother communication!
Stages
In this template, stages are defined that allow us to measure if response times are adequate, and even to set a maximum time limit. This way, a user could monitor response times, receiving alerts if an expected or maximum time passes in a specific stage, such as creation or review.
How to Optimize this Process for QMS Document Management
Qflow‘s flexibility allows extensive customization of processes created through templates or our AI Assistant. For example:
The “Document approval” template presented above can be edited by adding new tasks, conditions, or modifying the flow according to the specific needs of document management in a QMS.
For example, we can add a Document Approval task after the Review task to address the ISO 9001 requirement that documents must be approved by authorized personnel before publication. Approval ensures that documents are officially considered valid and accepted for use in the quality management system. Typically, this approval is carried out by the senior management of the company.
Additionally, we can add more data or fields to be completed in the forms without the need for programming.
For instance, in the initial step of Document creation request, we can include important document details such as code, document type (procedure, instruction, manual, among others), or the area or process to which it is related.
Deadline dates for the execution of each task (creation, review, and approval) can also be incorporated, and notifications and alerts can be set when deadlines are approaching.
Applying these modifications would result in a process flow as shown below, to which we added a pool with lanes to easily identify the responsible party for each task at a glance:
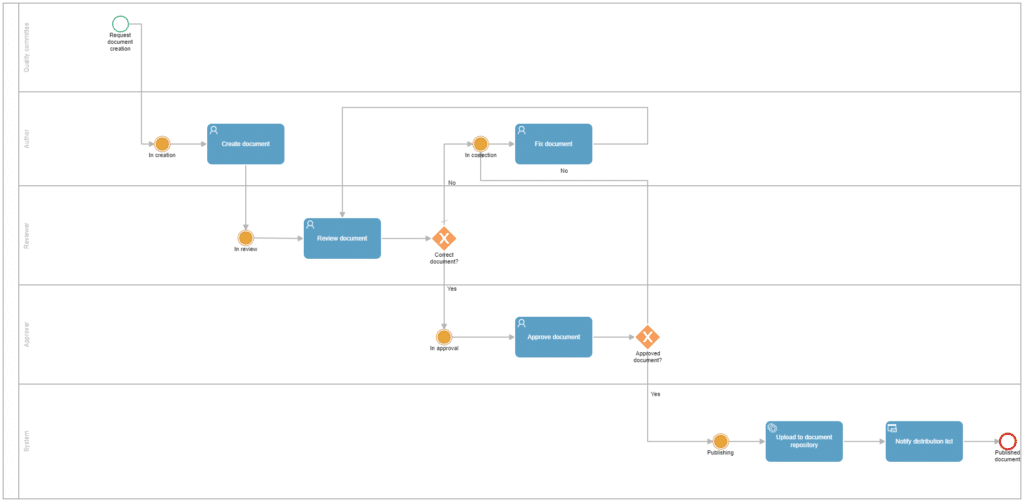
On the other hand, this process can be enhanced by incorporating a moderator role that receives pending tasks if the deadlines set for their completion have passed without being fulfilled. The moderator can then decide whether to grant new deadlines for completion or delegate the task to another person. While this can also be configured automatically in the tool, assigning this task to a user allows for a root cause analysis and determination of whether it is better to proceed in one direction or another.
New Document Version
The ISO 9001:2015 standard establishes specific requirements for controlling changes in the documents of the quality management system. This includes identifying changes, reviewing, and approving by authorized personnel before the publication of the new version, and implementing a system to clearly identify the current version of the documents. This ensures that people are using the correct and most up-to-date version of a document.
Taking the New document process as a basis, we can easily adapt it to create the New document version process.
Whether the documents are published in a document repository or hosted in Qflow, the starting point of the process can begin with a form that, based on a unique metadata of the documents, such as the code, searches for the current version of the document and brings it to the new process along with other metadata to be edited, maintaining the code and modifying the version.
Additionally, a text field is included to detail the changes compared to the previous version of the document, facilitating the tracking of changes for interested users.
From there, this process can follow the same steps as the New Document process, including creation, review, approval, publication, and distribution.
Quality action management
Quality actions are measures taken to correct or prevent problems associated with quality management. Managing quality actions is an essential task to ensure these measures are implemented effectively.
The automation of this process with BPM can help companies:
- Improve tracking of quality actions.
- Ensure timely implementation of quality actions.
- Evaluate the effectiveness of quality actions.
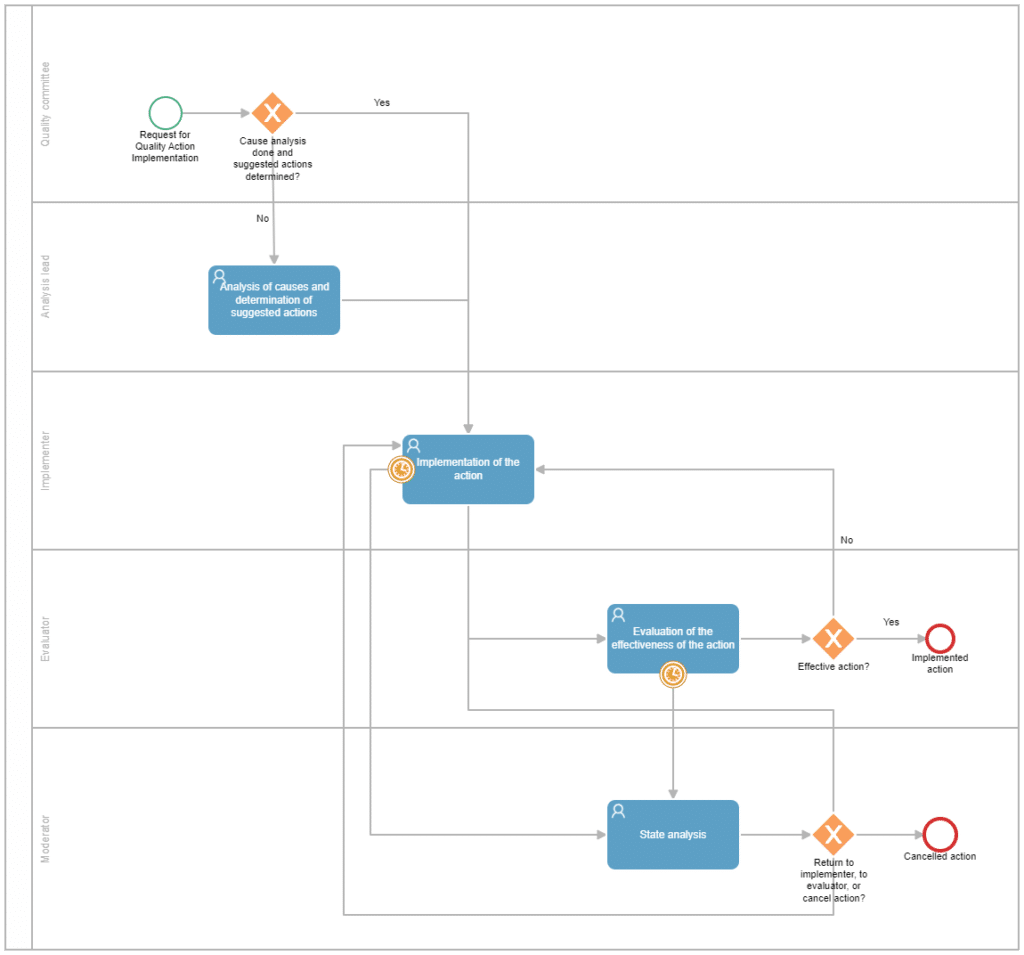
An automated quality action management process with BPM software could have the following steps:
Creation of a New Quality Action
In this initial step, the form can be easily configured to input relevant information for the process, such as:
- Name or description of the action to be taken.
- Type of action: corrective or improvement.
- Cause analysis.
- Suggested actions.
- Implementation deadline.
- Approval deadline.
Some basic data can be configured as required in this initial step (for example, the name or description of the action or the type of action), while others can be set as editable. This way, for example, I can optionally enter the cause analysis or suggested actions and determine, based on whether these fields are complete or not, the path the process will take.
The user who will take on the role of implementer and evaluator of the initiated action is also defined.
Assignment of the quality action to a responsible party for cause analysis and suggested actions
If, in the previous step, the user initiating the quality action process did not complete the cause analysis and/or suggested actions, the process will assign a task to a responsible party to complete both required fields.
This user can also edit the implementation and evaluation dates if, having defined the suggested actions, they believe the implementer needs more or less time to carry them out, or the evaluator needs time to assess the effectiveness of these actions.
Implementation of the quality action by an implementer
This is the task assigned to the user designated to carry out the suggested actions initiated on the date specified by the user initiating the process or the person responsible for cause analysis and determination of suggested actions.
They must provide implementation comments once completed and respond to the task for the process to proceed to the effectiveness evaluation step.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of the quality action by an evaluator
This task is assigned to the user designated to assess the effectiveness of the actions carried out by the implementer.
They must provide evaluation comments once completed and respond to the task, expressing their agreement for the process to conclude or requesting changes or the implementation of new actions if they believe that what has been implemented does not effectively address the cause that initiated the quality action in question.
Finally, similar to the document management process, this process can also be enriched by incorporating a moderator role. This role receives a task for status analysis if the deadlines set for the implementation or evaluation of the effectiveness of the action have expired without completion. The moderator can then decide to grant new deadlines for completion, delegate the task to another person, or cancel the action if it is deemed that its implementation has lost its relevance.
In the example shown below, you can see how the process flow would look in the Qflow tool, ready to be configured and automated!
Conclusions
These are just two examples of how to use BPM to automate quality management processes. With BPM, companies can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their quality management processes, leading to an overall improvement in the quality of their products or services.
If you want to delve deeper into these processes or explore other possibilities that Qflow can offer to support your QMS management, schedule a free demonstration today!