- 1. Which are the benefits of BPM?
- 2. Critical errors associated with inadequate business process management
- 3. What approach should business process management have?
- 4. Tools used in business process management
- 5. Advantages of Organizational Charts in Business Process Management
-
6.
Advantages of Using Business Process Management (BPM)
- 6.1. 1. Operational Efficiency
- 6.2. 2.Cost Reduction
- 6.3. 3.Service Quality Improvement
- 6.4. 4.Flexibility and Adaptability
- 6.5. 5.Transparency in Processes
- 6.6. 6.System Integration
- 6.7. 7.Continuous Improvement
- 6.8. 8.Knowledge Management
- 6.9. 9.Regulatory Compliance
- 6.10. 10.Improved Decision-Making
- 6.11. 11.Increased Business Agility
- 6.12. 12.Process Innovation
-
7.
Effective Strategies for Implementing Process Management in Your Company
- 7.1. Define the scope and objectives of the process management project
- 7.2. Choose the appropriate methodology and tool for business process management
- 7.3. Train and educate the process management team
- 7.4. Execute the business process management lifecycle
- 7.5. Evaluate and communicate the results of the process management project
- 8. Why Is Business Process Management So Underused?
- 9. Conclusion
Which are the benefits of BPM?
BPM, or Business Process Management in Spanish. A business process is a set of related activities carried out to achieve a particular goal, such as serving a customer, manufacturing a product, or sending an invoice. The operation of any organization depends on business processes, which determine how goods and services are produced and delivered to customers.
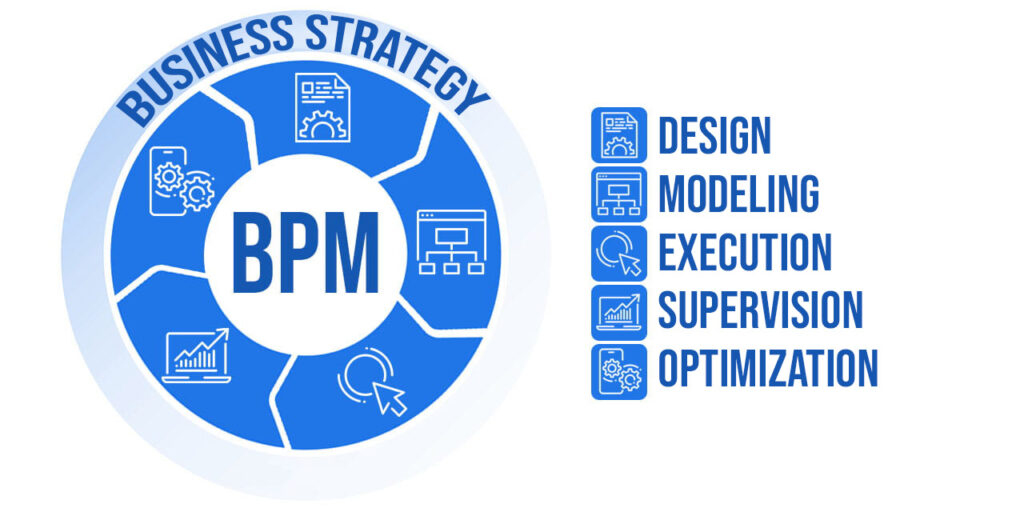
BPM is a methodology that involves analyzing, designing, executing, monitoring, and improving business processes systematically and continuously. The goal of BPM is to optimize process performance by reducing costs, errors, times, and risks while increasing customer, employee, and partner satisfaction.
Critical errors associated with inadequate business process management
Inadequate process management can lead to various critical errors that negatively impact productivity, quality, agility, and satisfaction of customers, employees, and partners.
Some of the critical errors associated with inadequate process management are:
Lack of control
When there is no person responsible for each process, or when roles, responsibilities, rules, and indicators for each process are not clearly defined, a lack of control occurs, preventing supervision, measurement, and correction of process performance.
Lack of knowledge dissemination
If processes are not documented, shared, updated, and employees are not trained, there is a lack of knowledge dissemination. This prevents employees from knowing, understanding, and following processes correctly, and hinders opportunities for improvement and innovation.
Lack of commitment
A lack of commitment occurs when workers do not perform their tasks with dedication and quality, and when they are not involved, motivated, and recognized for their participation in the processes, aligning with the organization’s strategy and objectives.
Lack of standardization
Lack of standardization occurs when processes are performed differently by different people or do not follow quality and efficiency criteria. This prevents processes from being consistent, repeatable, and comparable, reducing errors, variations, and redundancies.
Lack of timely and reliable information
A lack of timely and reliable information occurs when necessary data is not available to measure and control process performance, or when data is incomplete, inaccurate, or outdated. This prevents evidence-based decision-making and the implementation of corrective and preventive measures.
What approach should business process management have?
Business process management is an approach that seeks to improve organizational performance through the analysis, design, execution, monitoring, and improvement of business processes. BPM should consider the following elements:
Customer orientation
Processes should align with the needs and expectations of both internal and external customers, generating value for them.
Systemic vision
Processes should be considered part of an integrated and dynamic system that interacts with other processes, resources, environments, and stakeholders.
Continuous improvement
Processes should undergo an evaluation and feedback cycle to identify and correct deviations, inefficiencies, and improvement opportunities.
Innovation
Processes should be capable of adapting to and anticipating changes in the market, technology, legislation, and competition, generating creative and differentiating solutions.
Participation and commitment
Involving and motivating people who perform processes, as well as other stakeholders affected or benefiting from them, and fostering a culture of collaboration and learning.
Tools used in business process management
Business process management is a methodology that aims to improve organizational performance through the analysis, design, execution, monitoring, and improvement of business processes. Various tools can be used to facilitate the identification, representation, optimization, and control of processes. Some common tools include:
Pareto Chart
It is a bar chart that shows the most significant factors and their impact, ordered in descending order. It helps identify priorities and the most important issues to address.
Cause and Effect Diagram
It is a diagram that represents the possible causes that lead to a problem (effect). It has the shape of a fishbone and allows understanding the relationships between the factors involved in a process.
Flowchart
It is a diagram that shows the sequence of activities and decisions that make up a process. It allows visualizing the workflow, roles, resources, and critical points of a process.
Scatter Plot
It is a diagram that shows the relationship between two numerical variables. It allows analyzing the correlation, trend, and variability of data in a process.
Control Chart
It is a tool that allows recording and organizing process data. It enables measuring and controlling the performance of a process through the use of statistics.
There is no perfect approach or tool for all processes and situations, so it is important to make decisions that are suitable for the organization’s needs and the specific process.
Advantages of Organizational Charts in Business Process Management
Organizational charts are tools used to illustrate the structure and organization of a company, showing hierarchical relationships, departments, positions, and functions.
Business Process Management (BPM), a methodology that aims to improve the performance of business processes through analysis, design, execution, monitoring, and improvement, can benefit from organizational charts. BPM organizational charts have several advantages, including:
Clarity and visualization
They provide a clear and simple view of how the company is organized and how human and material resources are distributed. This facilitates the identification, understanding, and communication of business processes, as well as the identification of areas for improvement.
Coordination and collaboration
Defining roles, responsibilities, and lines of authority for each employee helps establish expectations, objectives, and indicators for each process. This promotes coordination and collaboration among different departments and stakeholders involved in processes, as well as accountability and feedback.
Planning and allocation
Organizational charts display the capacity and availability of each department and employee, enabling optimal planning and allocation of tasks and resources. This contributes to optimizing resource usage, reducing costs and times, and increasing process productivity and quality.
Adaptation and flexibility
Facilitating the updating and maintenance of the organizational structure allows for adaptation to internal and external changes that may affect processes. This leads to greater flexibility and agility in responding to market demands, customer needs, technological innovations, and legal regulations.

Advantages of Using Business Process Management (BPM)
Having a clear understanding of the benefits drives the necessary change. In this regard, we consider optimizing the use of resources, with an emphasis on activity planning, as fundamental. This means that to improve a company’s results, its processes must be enhanced.
Business Process Management (BPM) has several advantages:
1. Operational Efficiency
BPM identifies and eliminates inefficiencies in processes, such as redundant steps or bottlenecks, allowing tasks to be performed more quickly and effectively. This leads to resource optimization and improved productivity.
2.Cost Reduction
By improving process efficiency, companies can reduce costs related to downtime, errors, and rework. This includes savings in human and material resources, as well as operational expenses.
3.Service Quality Improvement
BPM allows standardizing and improving processes directly affecting the customer experience. This results in increased customer satisfaction and the ability to offer more consistent and high-quality services.
4.Flexibility and Adaptability
In a constantly changing business environment, BPM facilitates rapid adaptation to new market conditions, customer demands, or regulatory changes, enabling the agile modification of business processes.
5.Transparency in Processes
BPM provides a clear and detailed view of business processes, facilitating the identification of improvement areas, problem resolution, and understanding of how each process contributes to the overall objectives of the company.
6.System Integration
Business process management helps unify and coordinate different systems and applications used in the organization. This improves communication between departments and systems, facilitating a more coherent and efficient workflow.
7.Continuous Improvement
Process management is not a one-time effort but a continuous process. It allows organizations to regularly assess and improve their processes, adapting to new best practices and technologies and fostering a culture of continuous improvement.
8.Knowledge Management
By documenting and standardizing processes, BPM helps preserve critical business knowledge. This is especially useful for training new employees and maintaining consistency in process execution.
9.Regulatory Compliance
Ensures that business processes comply with current regulations and laws. This is crucial to avoid fines and sanctions and to maintain the company’s good reputation.
10.Improved Decision-Making
With precise data and detailed analysis provided by BPM, business leaders can make more informed and strategic decisions, relying on real and updated information about process performance.
11.Increased Business Agility
BPM provides companies with greater responsiveness to market opportunities and challenges. It allows for a quick reconfiguration of processes to take advantage of new opportunities or face unexpected threats.
12.Process Innovation
By analyzing and restructuring existing processes, business process management can reveal opportunities for innovation. This can lead to the creation of new products, services, or work methods that can give the company a significant competitive advantage.
Effective Strategies for Implementing Process Management in Your Company
Process management in a company is a methodology that seeks to improve the performance of business processes through their analysis, design, execution, monitoring, and improvement.
To implement process management in a company, the following steps can be followed:
Define the scope and objectives of the process management project
Identify the processes to be improved, existing problems and opportunities, objectives and indicators to be achieved, and priorities and resources available.
Choose the appropriate methodology and tool for business process management
Select the philosophy and software that best fit the needs, expectations, and capabilities of the company. Different options exist, such as the BPM model, Lean Manufacturing, Six Sigma, among others.
Train and educate the process management team
Select individuals to participate in the project, assign roles and responsibilities, and provide the necessary training and support for them to perform their functions effectively and efficiently.
Execute the business process management lifecycle
Follow the phases of analysis, design, execution, monitoring, and improvement of the selected processes, using the chosen methodology and tool, and adhering to best practices and quality standards.
Evaluate and communicate the results of the process management project
Measure and analyze performance indicators, compare results with objectives, identify lessons learned and best practices, and disseminate achievements and recognitions among participants and stakeholders.
Why Is Business Process Management So Underused?
There are various reasons why business process management is inefficient. The key lies in the lack of awareness of the appropriate tools, as well as the tangibility of the benefits of proper implementation.
However, many companies do not apply this methodology or do so partially or incorrectly. Some possible reasons include:
Lack of knowledge
Many companies are unaware of what business process management is, how it works, what benefits it offers, and how to implement it correctly. This may be due to a lack of training, information, or interest on the part of executives and employees.
Lack of resources
Many companies do not have the necessary resources to implement business process management, such as time, money, personnel, technology, or external support. This may be due to a lack of planning, prioritization, investment, or change management.
Lack of commitment
Many companies do not have a real commitment to business process management, either from management, employees, or customers. This may be due to a lack of vision, communication, motivation, or involvement.
Conclusion
Process-based management is now crucial for the survival and success of a company in today’s economically complex and globally competitive environment, marked by continuous innovation and increasing digital transformation.
Today, it is essential to streamline organizations with administrative modernization that leads to more efficient communication and management, away from rigid bureaucratization. This results in a more competitive and profitable business entity with higher quality indices.
Process automation tools are an efficient and well-tested shortcut.
The challenge lies in embracing change.






