What is Business Process Management, Lifecycle, Strategies and More
A business process is a set of activities that help a business achieve a specific goal. However, business processes are often inefficient and need improvements to reduce errors and costs. This is where business process management (BPM) comes into play.
A business process management (BPM) evaluates the existing processes and looks for ways to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and lower costs. It is a continuous process that can gradually elevate the business outcomes with time. In this guide, we will talk in detail about what business process management is and cover its lifecycle, strategies, and more.
What is Business Process Management or BPM?
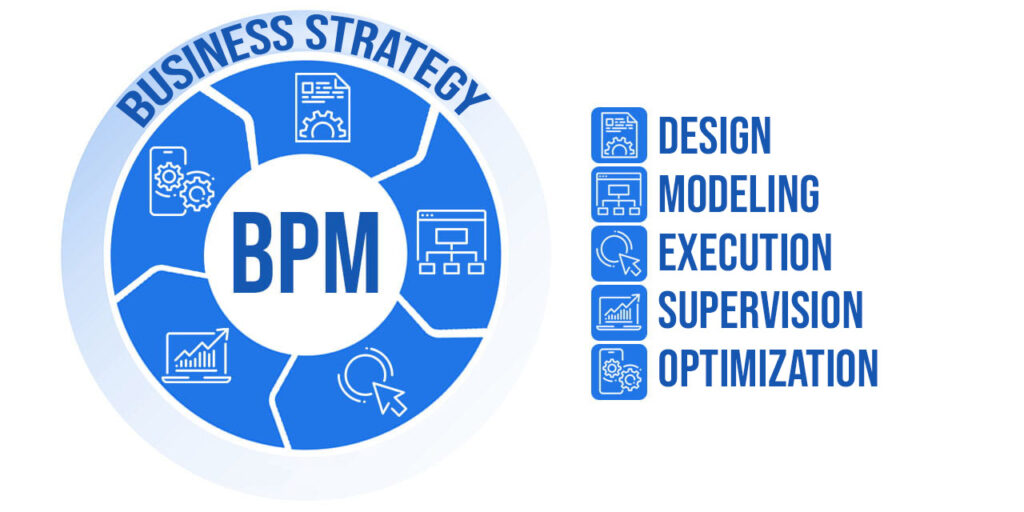
Business Process Management (BPM) is a structured approach to improving business processes. It involves an activity or set of activities for analyzing, designing, modeling, executing, supervising, and optimizing business processes to meet specific business goals, such as improving customer experience and increasing profits.
BPM observes the whole end-to-end process and continuously reengineers it to increase efficiency and reduce costs. It leverages activity monitoring, advanced analytics, and decision management capabilities to coordinate systems and people to meet business outcomes.
Overall, BPM aims to optimize process performance by reducing costs, errors, times, and risks while increasing customer, employee, and partner satisfaction.
What is its importance?
Well-structured and efficient processes are the key to business success, and that’s what Business process management (BPM) is entitled to offer.
There are hundreds of tasks involved in different business operations, such as developing products, fulfilling orders, handling customer service, managing employees, and more. These processes involve systems, people, and technology. When these business operations are well structured and broken into smaller, repeatable steps, they lead to efficient operations and consistent outcomes. And that’s what businesses can get with BPM.
BPM can analyze, model, execute, and optimize business processes/operations to maximize their outcomes while reducing resource use. Since BPM involves continuous process improvement, it also helps businesses adapt to changing needs.
The few key reasons why BPM is crucial for businesses include the following:
- Increase efficiency and reduce waste
- Reduce cost and enhance quality
- Uplift employees’ productivity
- Increase agility
- Enhance visibility
- Improve customer satisfaction
- Elevate adaptability
- Standardize processes
- Competitive advantage
In short, BPM is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their processes and achieve long-term success.
The Lifecycle of Business Process Management
Business process management (BPM) involves multiple stages in its workflow. Therefore, it’s important to define those stages in order to have a structured way of process improvement and proper progress tracking. In this perspective, the BPM lifecycle goes through the following five stages:
Stage 1. Design
The first stage is to outline the scope and boundaries of the process. The main activities involved in this stage include:
- Identify the process to optimize.
- Identify individual tasks within the process.
- Define goals and requirements.
- Define task owners for each task.
Overall, this stage lays the foundation for the remaining BPM lifecycle stages. So, it should be well-defined so that the team can intelligently look into the process and identify the improvement areas.
Stage 2. Model
The second stage in the BPM lifecycle is creating the process visual representation. It will act as a blueprint and clarify how a process executes. The visual representation should reflect process flow, timelines, inputs/outputs, activities/tasks, data flow, etc. The team can use a BPM tool like Qflow to easily create a visual representation.
Stage 3. Execute
This stage involves testing the process with a limited group. The team can assign tasks to a few task owners and provide them with the necessary resources. Afterward, the team can monitor progress and incorporate feedback. Once the execution goes well, the process is all set to be implemented for a broader audience.
Stage 4. Monitor
This stage is all about monitoring the process and measuring efficiency improvements. It also involves looking for areas to improve or fixing any underlying issues. The team can set key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor the process.
Stage 5. Optimize
The last stage in the BPM lifecycle is optimization. In this stage, the team undergoes final process adjustments to optimize the efficiency.
Overall, the BPM lifecycle is all about thorough planning, deep monitoring, and regular optimization to get the best outcomes from business processes.
Strategies for Business Process Management
The BPM lifecycle outlines all the key stages to execute BPM, but business process management strategy goes beyond just following the lifecycle stages. It requires support from the stakeholders and commitment from employees to optimize processes. Therefore, below are the key strategies to follow to implement BPM:
1. Present Benefits to Stakeholders
Start with presenting the benefits to stakeholders. Explain to them the necessity of BPM and what benefits the team intends to achieve, such as improving product quality, optimizing operational efficiency, or reducing cost.
2. Select the Process
Look for the process that is in severe need of improvement, whether it is related to hefty cost, bottlenecks, inefficiencies, etc.
3. Get Endorsement from Leadership
To motivate team members, get the endorsement from leadership. Their willingness toward BPM will encourage the team to show full dedication in the whole BPM lifecycle.
4. Execute Process Improvement
Head for the process improvement by modeling the process and then executing it with a limited group. Endorse the feedback and make the process available for a larger group.
5. Measure Results and Disclose Outcomes
Regularly monitor the progress outcomes through set KPIs and optimize where necessary. Also, the team should disclose the fruitful outcomes to stakeholders/leadership so that they get an endorsement to follow a similar business process management strategy for other processes.
Why is there so little management…?
Although business process management (BPM) offers many benefits to businesses, its use is still not so common. There are a limited number of organizations that leverage the BPM strategy in their processes. Some possible reasons why BPM is less common include:
1. Lack of Knowledge
Many companies are unaware of what business process management is, how it works, what benefits it offers, and how to implement it correctly. This may be due to a lack of training, information, or interest on the part of executives and employees.
2. Lack of Resources
Many companies do not have the necessary resources to implement business process management, such as time, money, personnel, technology, or external support. This may be due to a lack of planning, prioritization, investment, or change management.
3. Lack of Commitment
Many companies do not have a real commitment to business process management, either from management, employees, or customers. This may be due to a lack of vision, communication, motivation, or involvement.
Conclusion
To conclude, business process management is the key to increasing organizational value by improving processes. By strategic modeling, executing, and optimizing business processes, BPM helps businesses have well-structured operations with increased efficiency and cost savings. Therefore, it’s time to leverage BPM for your business processes and start your journey toward operational excellence. Try Qflow now and change your business process management game!