Introduction to Q-flow sites
Introduction
The objective of this tutorial is to give a brief introduction to each of the Q-flow sites.
Q-flow is a tool used to define, automate and manage business processes or business workflows.
It comprises 4 sites:
BPM
Q-flow site
OMM
SAM
What to do inside each one is described below:
BPM: Business Process Web Designer
This site allows you to design flows and then use them.
In order to create the flow, a sub package must be created within the “Root” package. Inside this sub package, flow templates are created.
Within each flow template different items may be defined for the flow such as, “application data”, “template roles”, “data domains”, “integrations”, “event handlers”, “validations”, “bots” and “application parameters”.
Definition of some of the items:
Within “Application data” different data is defined that provides structured information of the process. Each datum is associated with a domain, these may be already defined (number, text) or new ones may be created within “data domains”.
Application data:
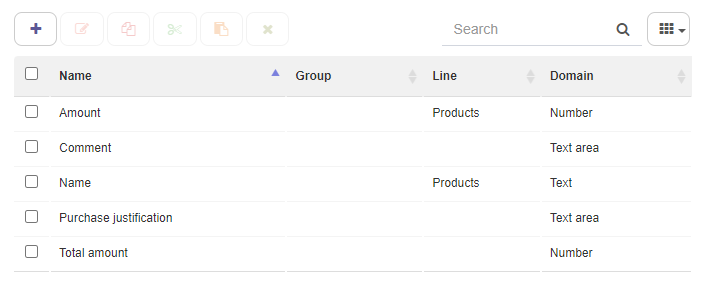
Data domains:
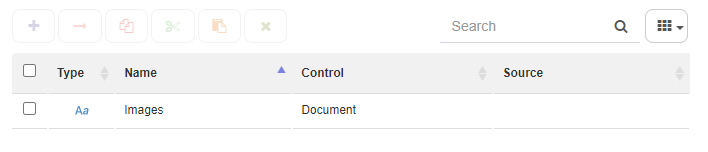
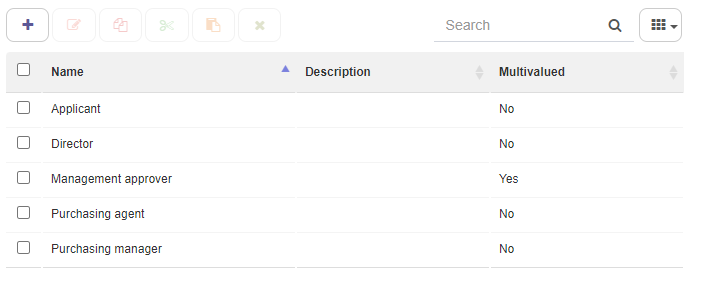
Template roles are used as recipients for interactive steps. Roles are associated with users and Q-flow will assign them a task when the process reaches an interactive step. It may be a single user or several if the roles are multi-valued.
Within “integrations” other systems may be invoked.
For more details on the rest of the items, consult the Business Process Web Designer manual.
The flow is defined by different elements, such as events, tasks, gateways connected to each other, among others. The elements have different types, for example the tasks may be a user task, formula, etc.
Template example:

Each step has different settings depending on the assigned type. For example, the user task allows the interaction between users by submitting a question that must be answered. The question and its possible answers are defined in the task properties.
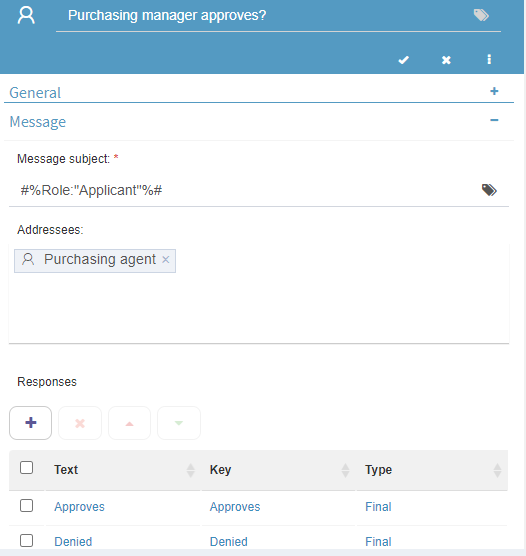
In the above example the purchasing agent, purchasing manager and director are asked if they approve of the requested expense.
Q-flow site
This site allows you to start and track flows.
Different operations may be performed such as starting flows, answering questions or pending tasks, and viewing received notifications.
The processes are started within the “Start flow” section. In it, all the templates that have a production version are available.
Example of a flow form:
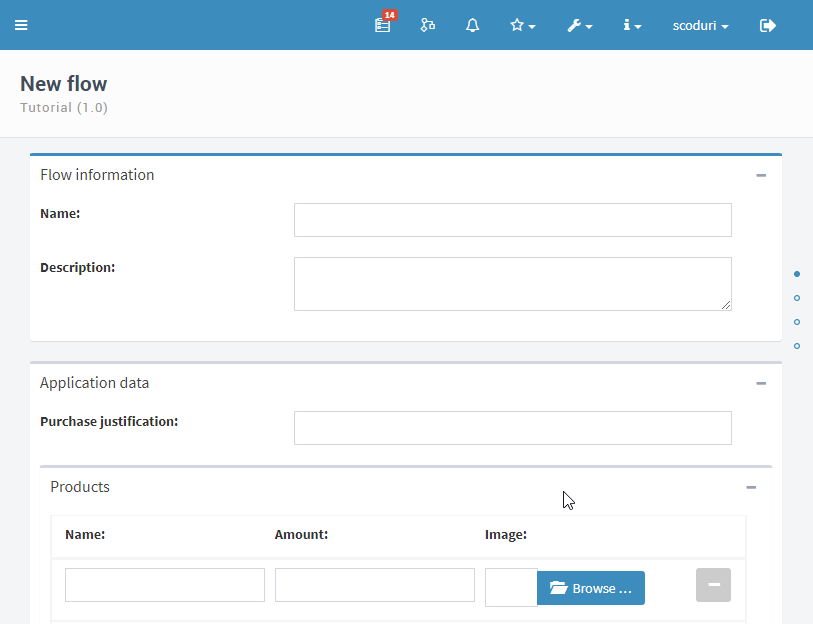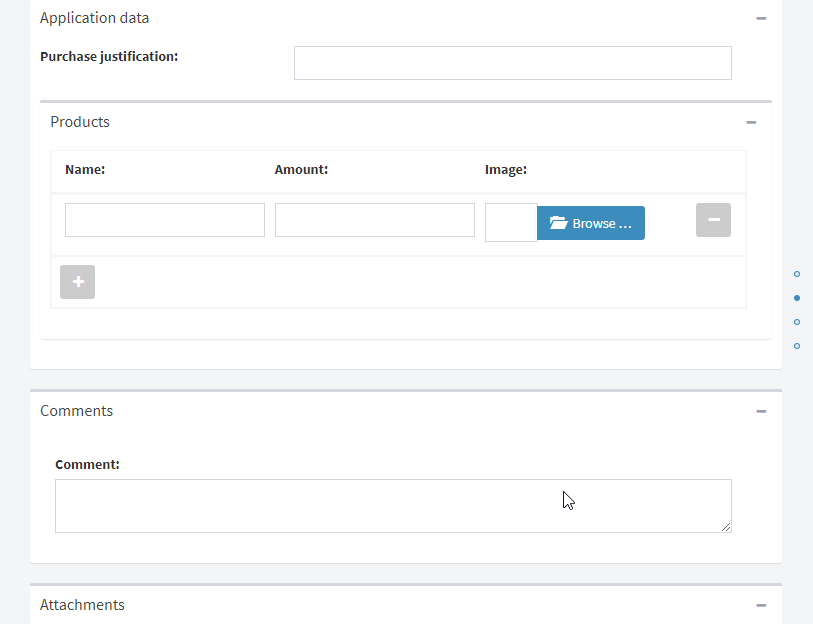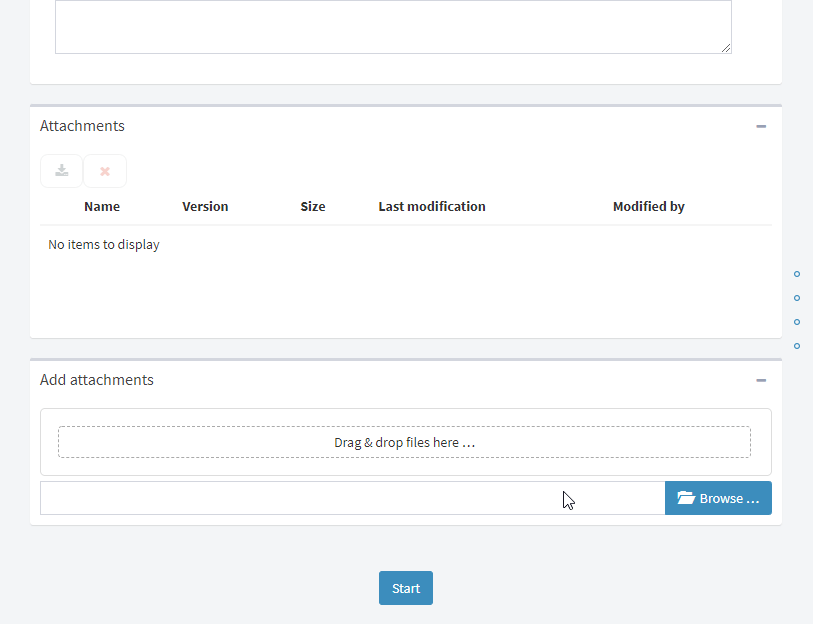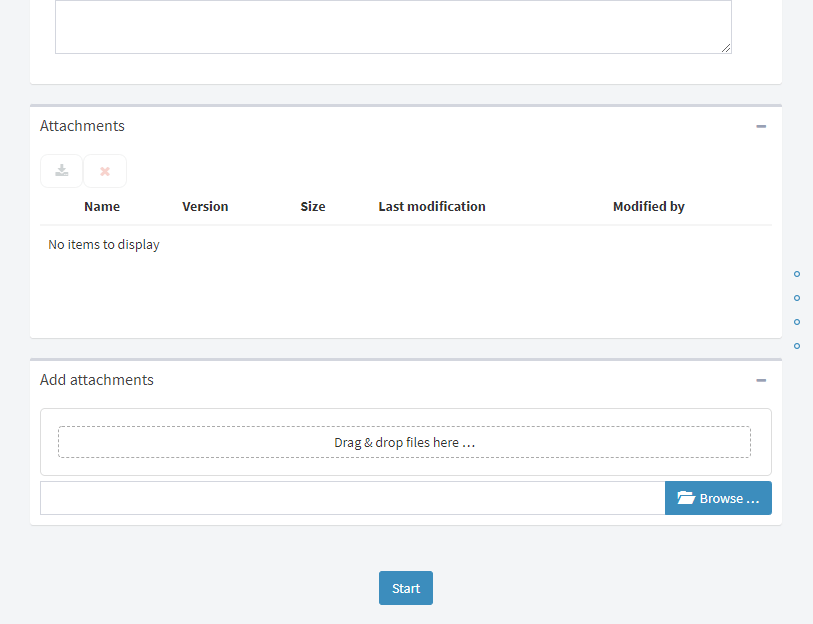
The flow information may be displayed in views, charts, indicators and dashboards.
Views: within this section different custom views may be created that show only the data of the desired flows.
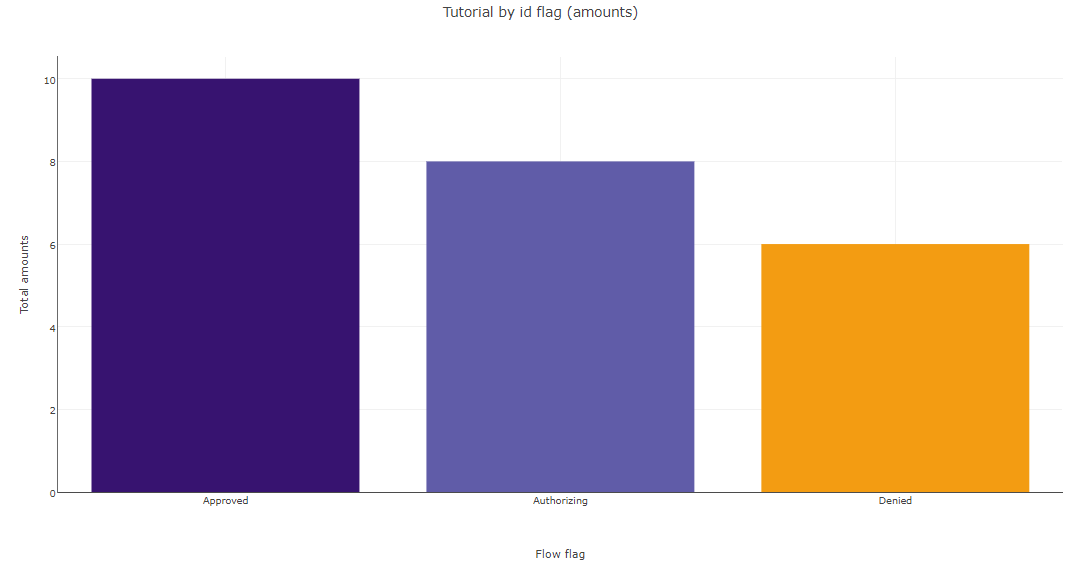
Charts: different custom charts may be created to visually track flows.
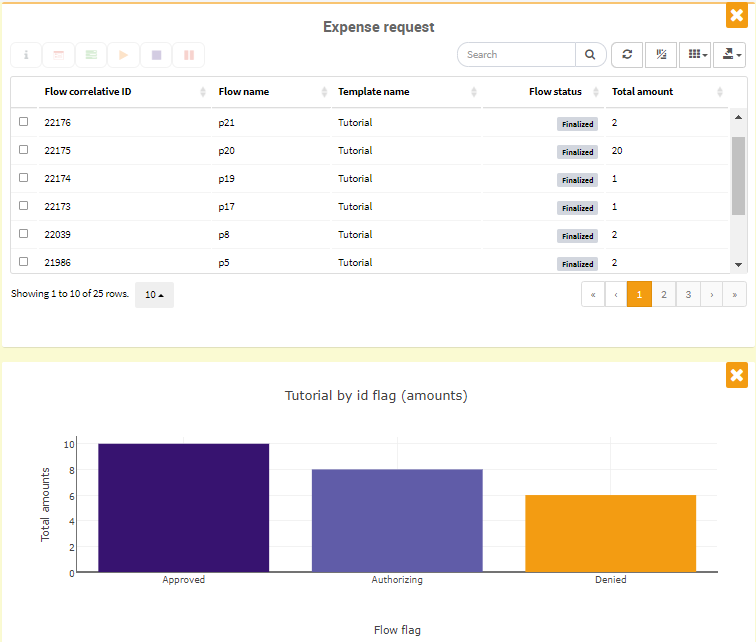
Dashboard: the information is displayed in views, charts and indicators in an orderly manner so that the user can view everything at once.
OMM: Organizational model management
This site is used to represent the structure of the organization and its members in the system. Different user properties may be configured and it is possible to manage configuration aspects.
The organizational model handles three types of members, nodes, groups and users.
The nodes are used to organize the structure of the organizational model in a hierarchical way. There is a node that is the root of the structure. A node may contain groups and users. Users may be organized in a way analogous to the real structure of the company.
Groups allow you to group users who share certain properties. They contain not only users but groups may contain other groups. They are often used, for example, to group users who fulfill the same function.
The users represent the Q-flow users. A user may be a member of multiple groups, but cannot be in more than one node.
Within each node users and groups may be created.
Within the site, different configurations may be created, such as managing tool permissions, calendars, security roles, security providers, login reports and permission audit.
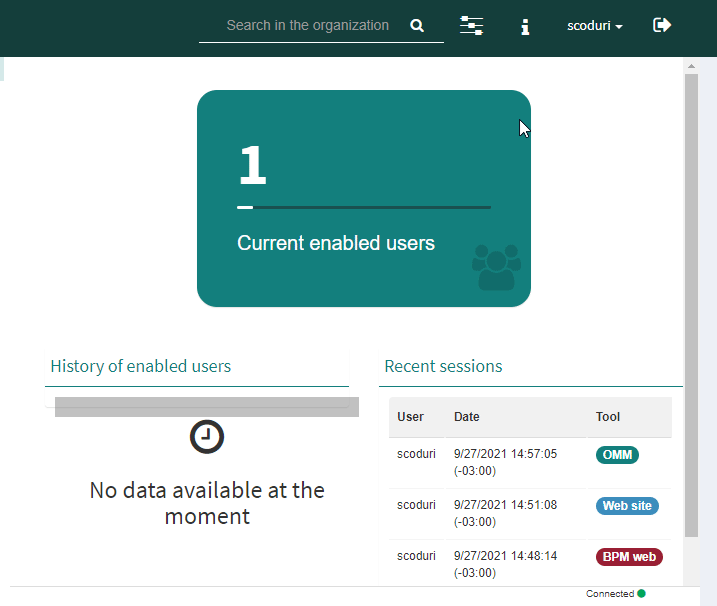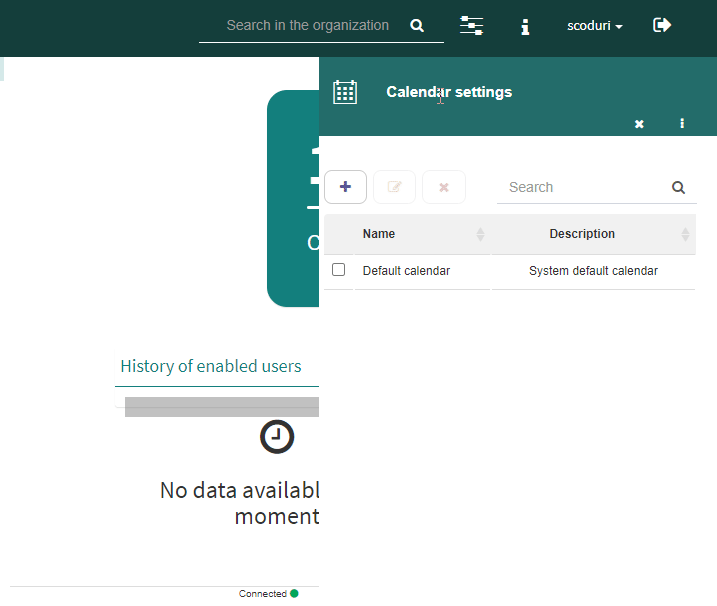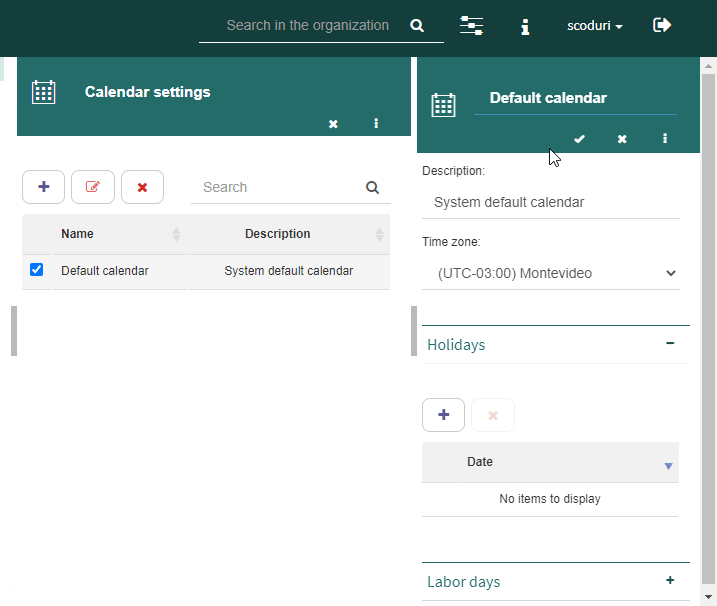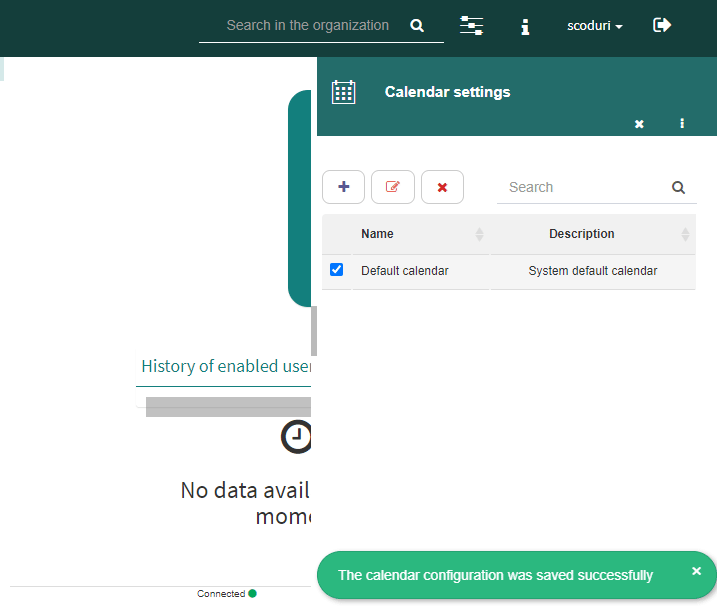
The “Calendars” option allows you to define different calendars so that different users may use them. This is a useful tool, for example, when organizations have affiliates in several countries and therefore, those affiliates are guided by different calendars (holidays, work regime, etc.).
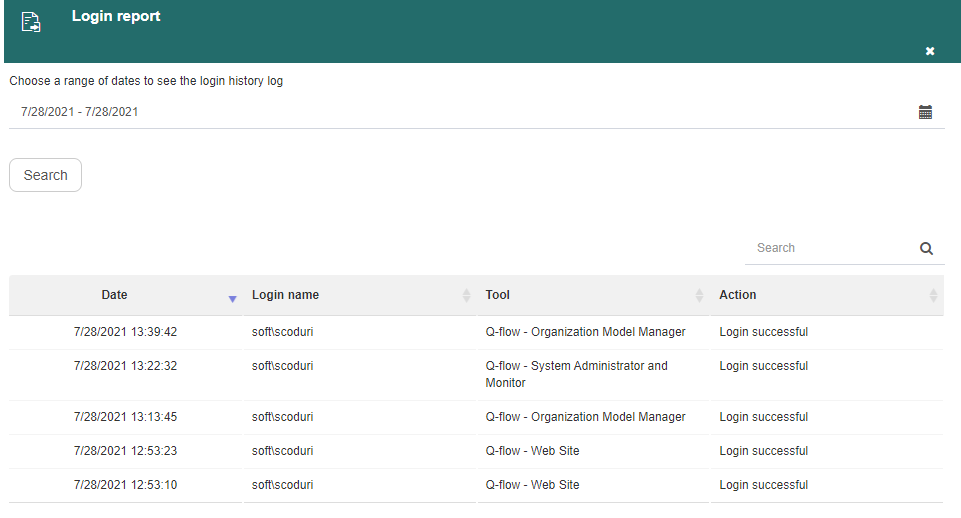
The “Login report” option shows which users have logged into a Q-flow tool in a certain period of time. Logouts and failed attempts to log in are also displayed.
SAM: System administration and monitoring
This site allows you to configure aspects that are system-wide, different elements that affect the general operation such as services and sites, extended properties, licenses, notification senders and system parameters.
From the service statuses all Q-flow services and sites may be monitored, such as whether they are working normally or not.
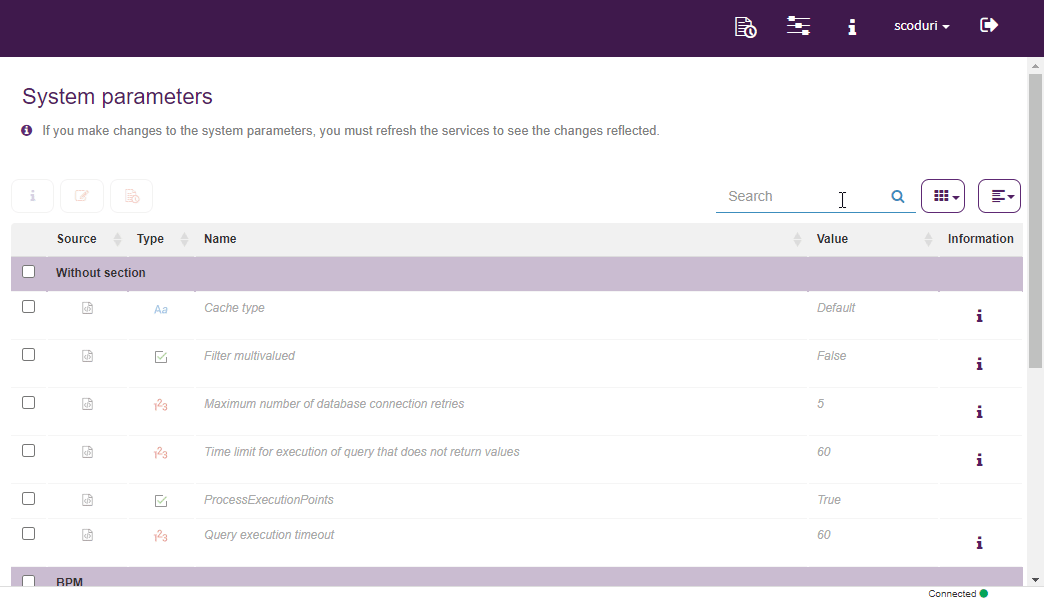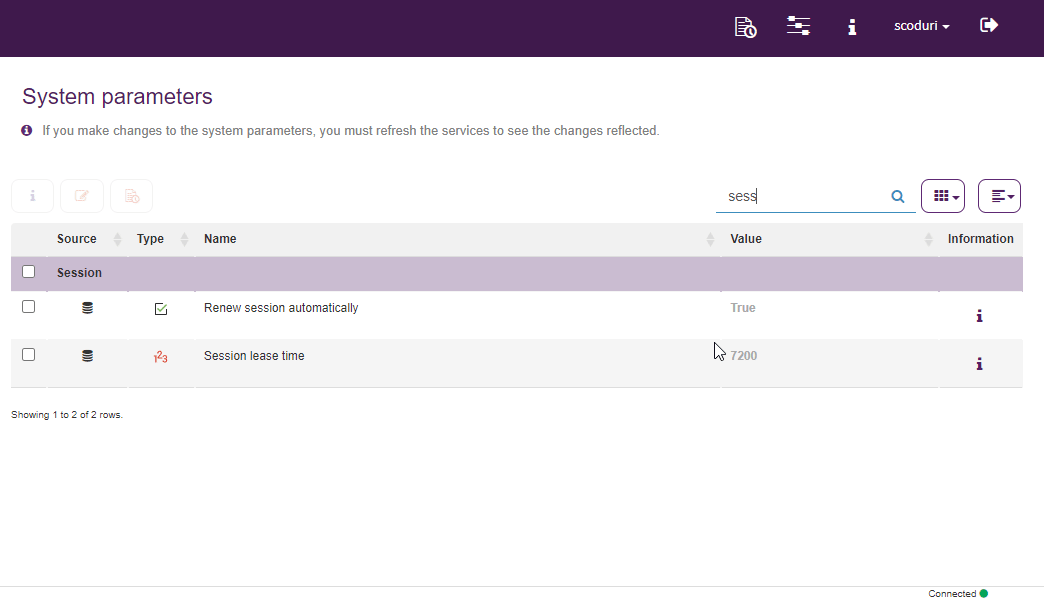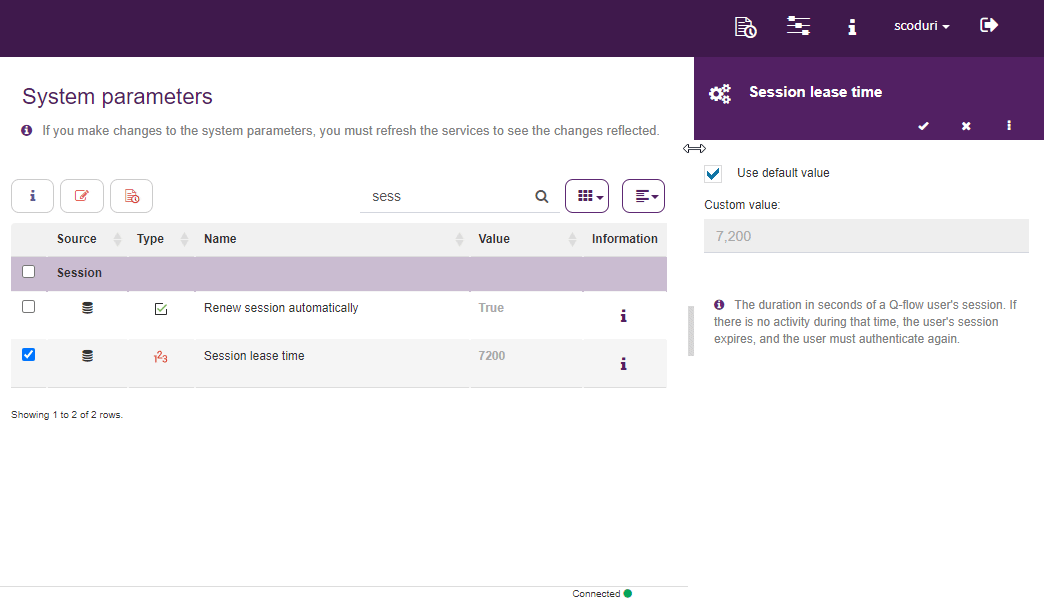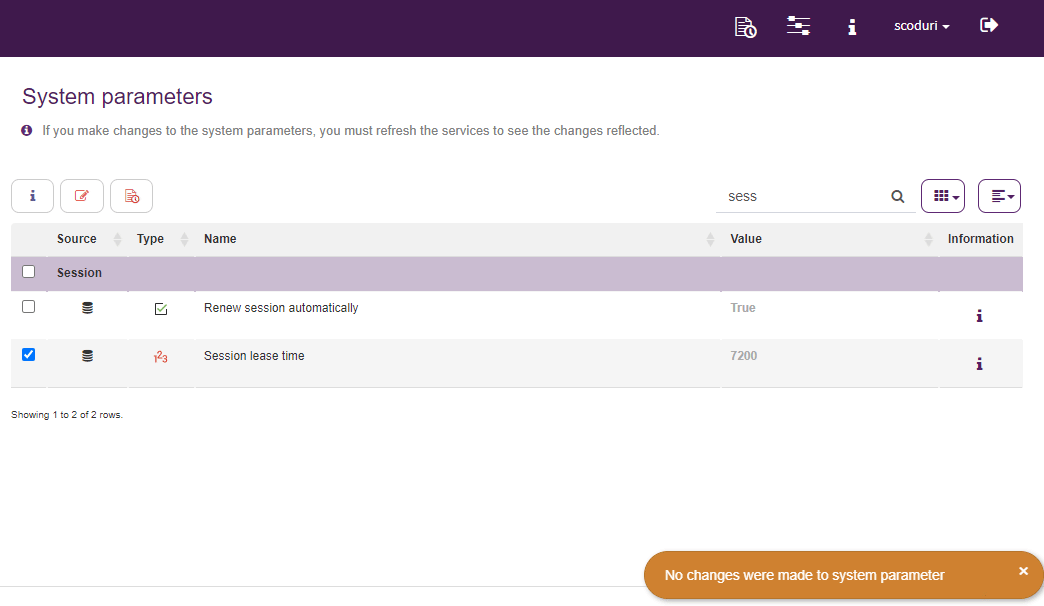
System parameters may be modified, they can control various aspects of the product’s operation. For example, the duration of the session may be managed as well as allowing the login with Microsoft or Google, among others.
The extended properties are defined by the organization and are displayed in the properties panel of each member of the organizational model (user, group and node), in the model manager.
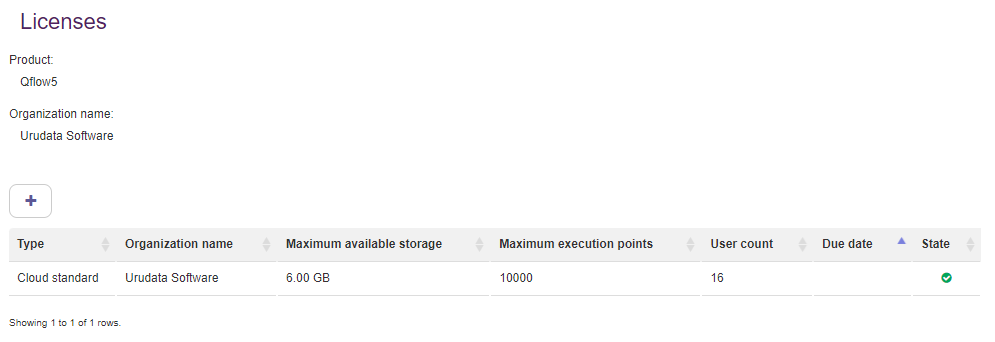
Q-flow licenses may be managed. You can see which ones are valid, which ones have expired, add new ones and check their usage.
Multi-tenancy installations are supported. This adds a new level of the organization in the system, therefore, the same server and the same database may host different environments with their own data, only sharing global configurations. In this new system, there is a main tenant and a number of secondary tenants which may be managed from this section.
The notification senders section shows the senders. Senders may be managed, added, edited or deleted.
Finally, for more information on each of the sites, you can see their respective manuals that explain their use in greater depth:
Web site manual