Introduction to Qflow tools¶
Introduction¶
The aim of this tutorial is to give a brief introduction to Qflow and each of its tools.
Qflow is a platform for defining, automatizing and managing business workflows.
It consists of 4 tools
Qflow Design
Qflow Task
Qflow Team
Qflow Admin
Qflow Access portal enables users to enter each tool, as well as their respective manuals and tutorials.
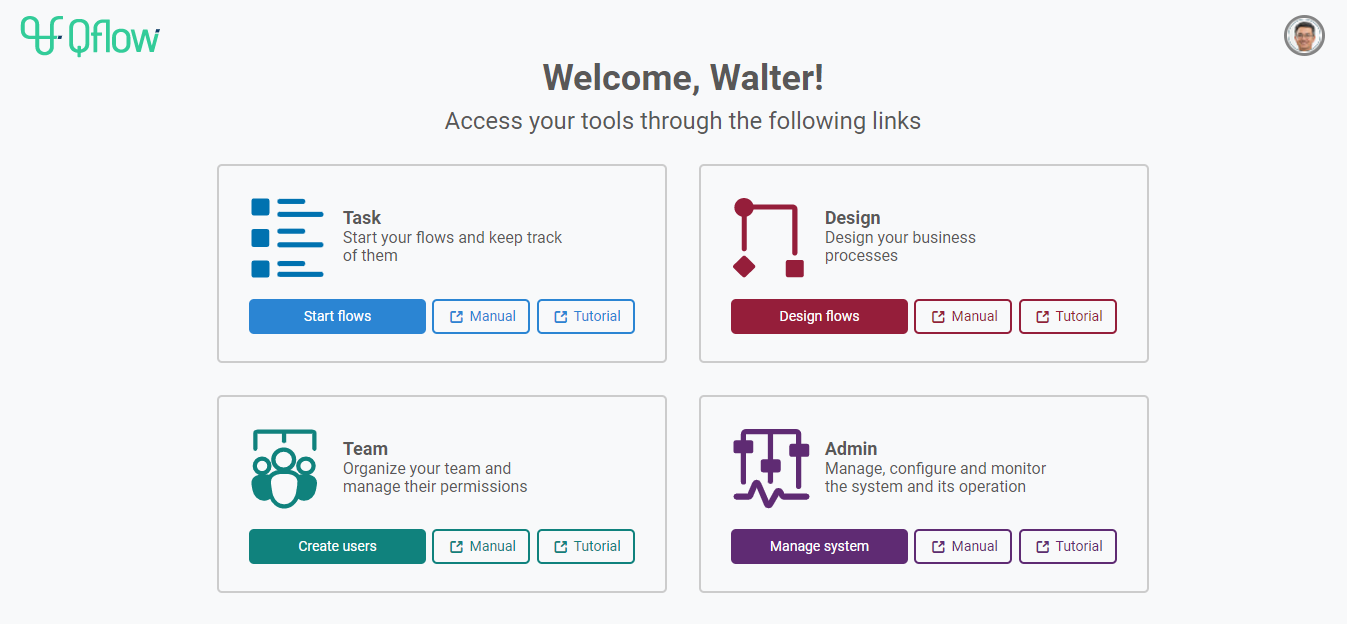
Fig. 56 Qflow Access¶
Brief descriptions for each tool’s features are listed below.
Qflow Design: business workflows web designer¶
This tool is designed for creating customized workflow solutions, aimed at adapting to clients’ needs.
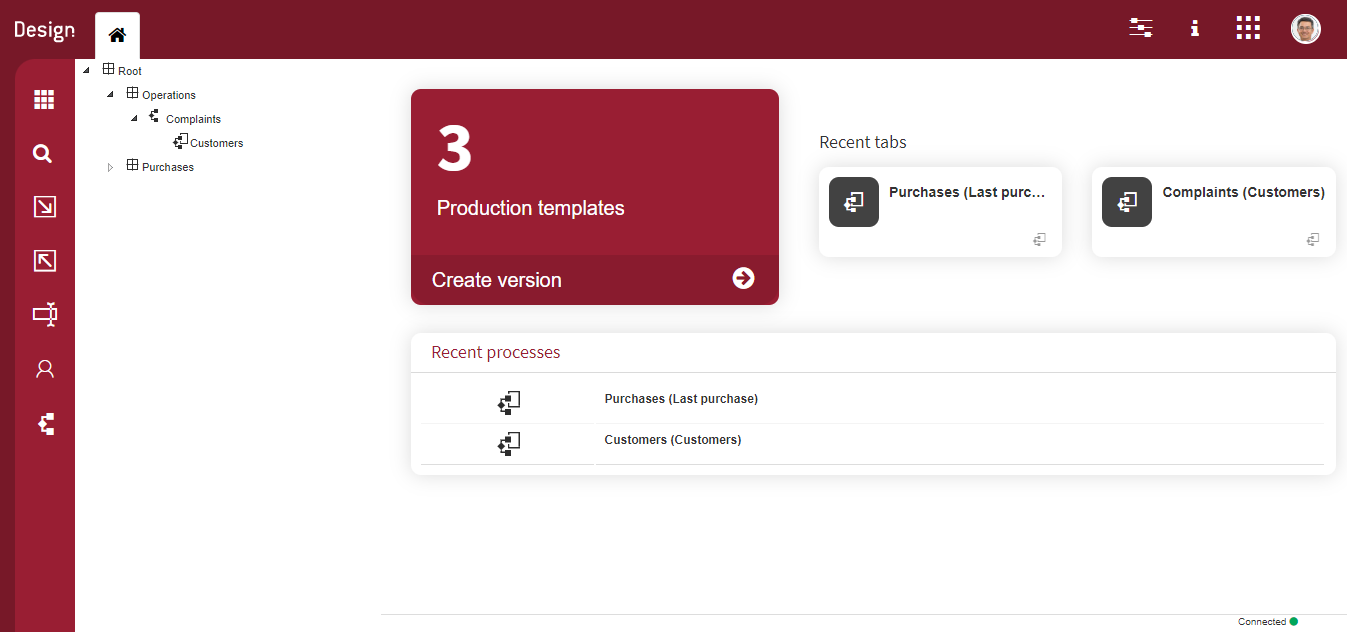
Fig. 57 Qflow Design¶
In order to start creating processes, one must access the packages tree located in the tool’s left panel. The “Root” package can be found there, and sub-packages representing the different organization’s areas can be created within it. Once positioned in the process’s desired route, the process template must be created.
Multiple properties (items) can be created within each process template. Some examples of it are “Roles”, “Application data”, “Data domain”, “Integrations”, “Event handler”, “Validations”, “Bots”, “Application parameters”, etc.
Brief details regarding some of the items:
Within Application data one can store structured information regarding the given workflow. Each piece of information must be associated with a corresponding Data domain, either by using those which have already been defined (text, number), or by creating new ones.
Application data
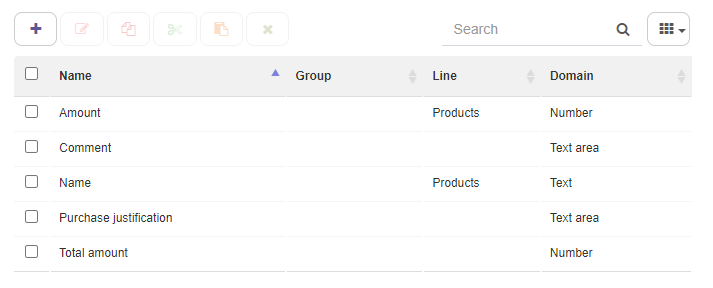
Fig. 58 Application data list¶
Data domain
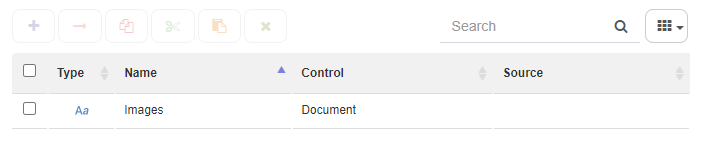
Fig. 59 Data domain list¶
Process roles function as addressees within flows’ interactive steps. Once a certain user is assigned to a process role, Qflow will automatically assign them a task each time an interactive step is reached within the given workflow. Multivalued process roles can be assigned to multiple users.
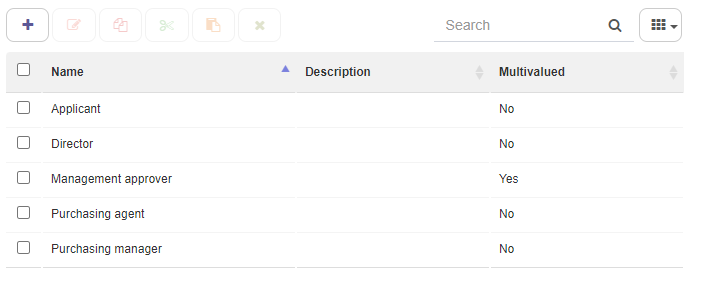
Fig. 60 Process role list¶
Other systems can be invoked within Integrations.
For more details regarding Items, please see the following manual: Qflow Design.
Processes can be defined regarding multiple elements as can be events, tasks, gateways, etc. Additionally, each element can bear different types. For instance, tasks can be User Tasks, Formulas, etc.
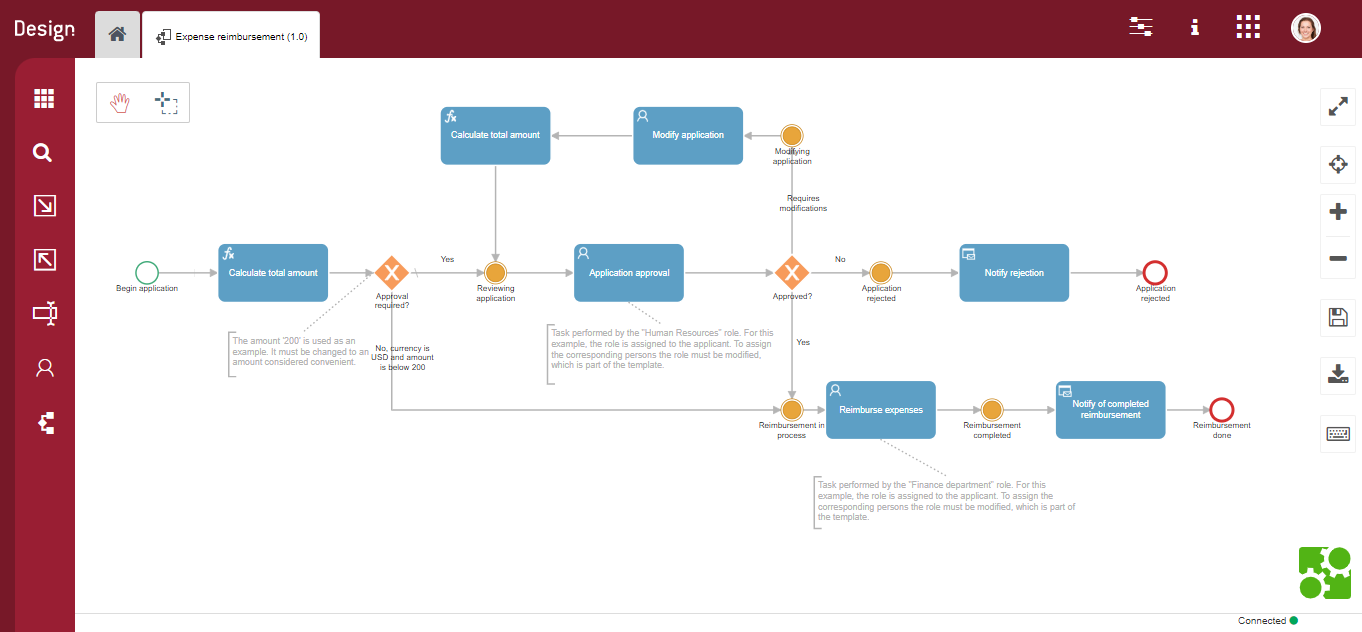
Fig. 61 Expense reimbursement flow template example¶
Flow steps have different configurations, depending on the type they were assigned. For instance, User Tasks allow user interaction by sending questions with their corresponding possible answers. These can be set within the task’s properties.
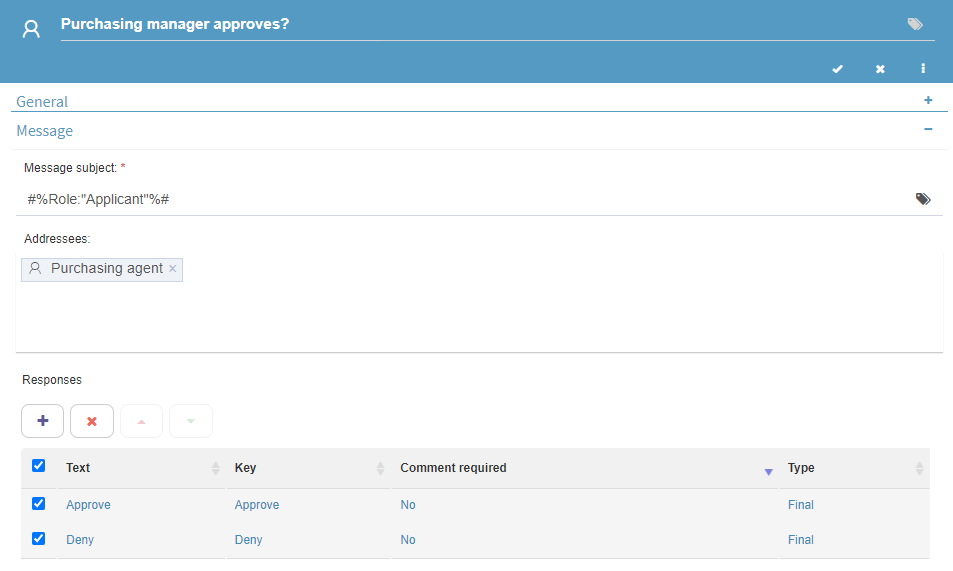
Fig. 62 User task type example¶
Within the given flow, the Purchasing Manager is asked whether they approve the applicant’s expenses.
Qflow Task: processes and tasks tool¶
This tool enables users to start and monitor flows.
Fig. 63 Qflow Task¶
Several operations can be carried out. These range from answering pending tasks or queries, to reviewing notifications, starting flows, etc. Processes are started within the “Start process” section. Available templates bearing a production version can also be found there.
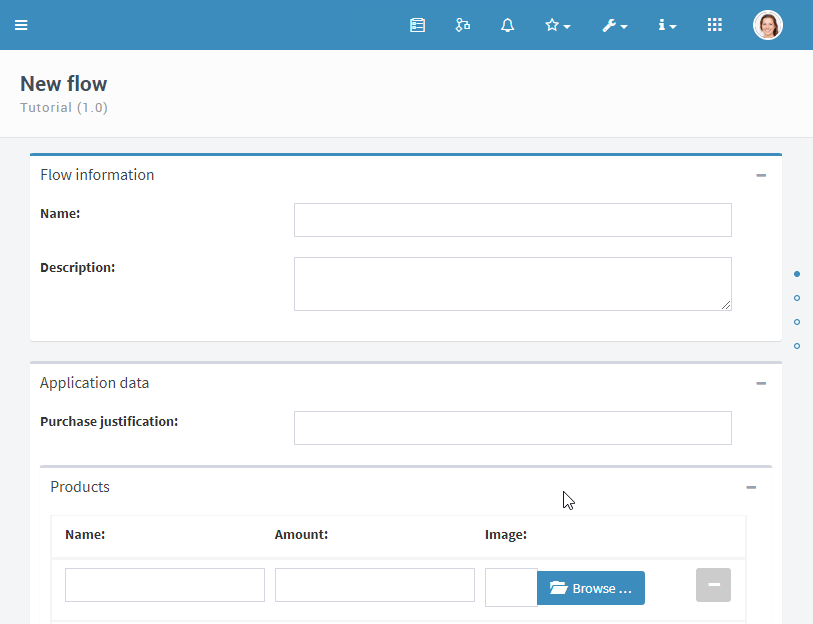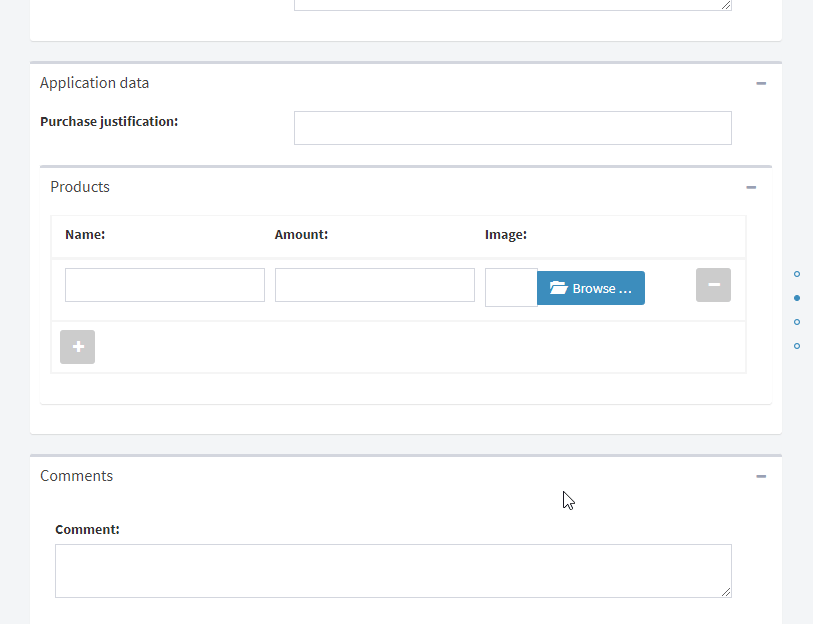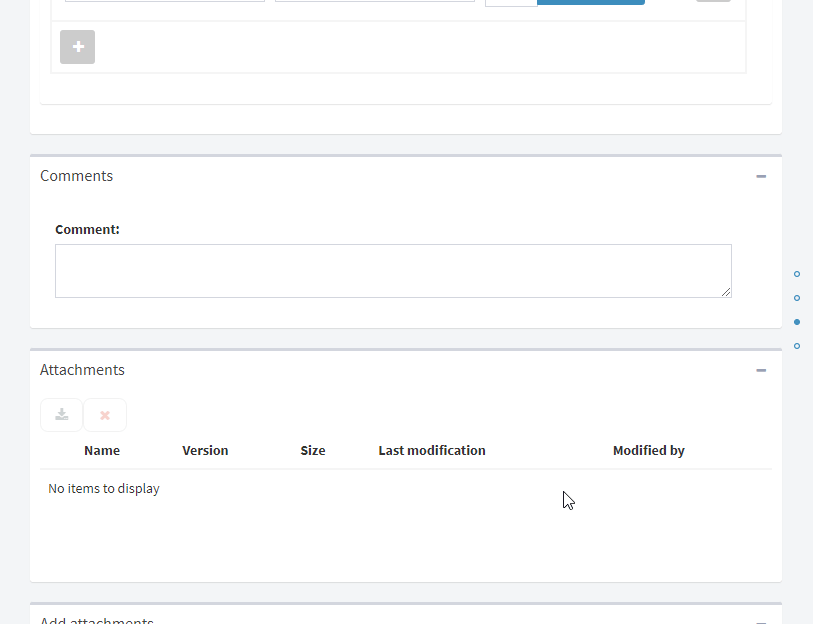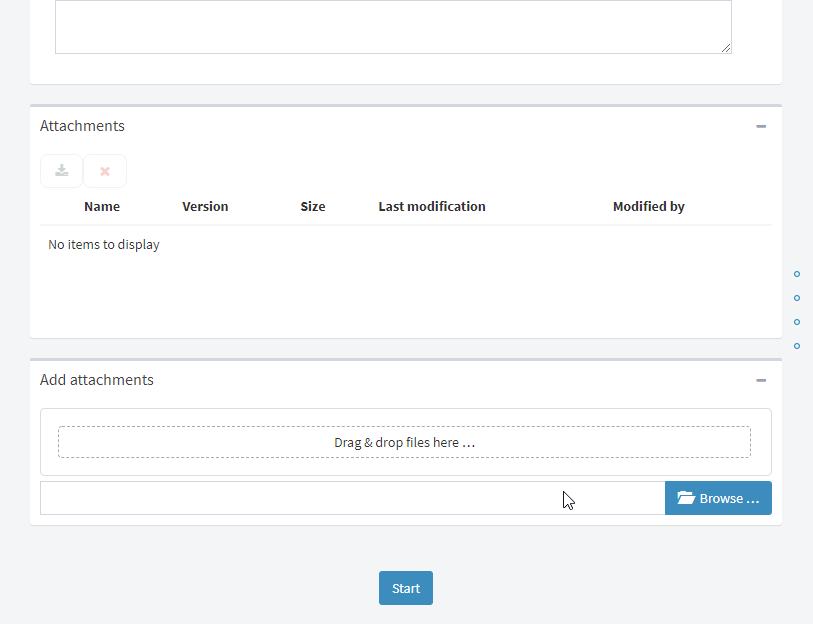
Fig. 64 Flow form example¶
Flow information can be seen through views, charts, KPIs and dashboards.
Customized information views for each desired flow can be designed within the Views section.
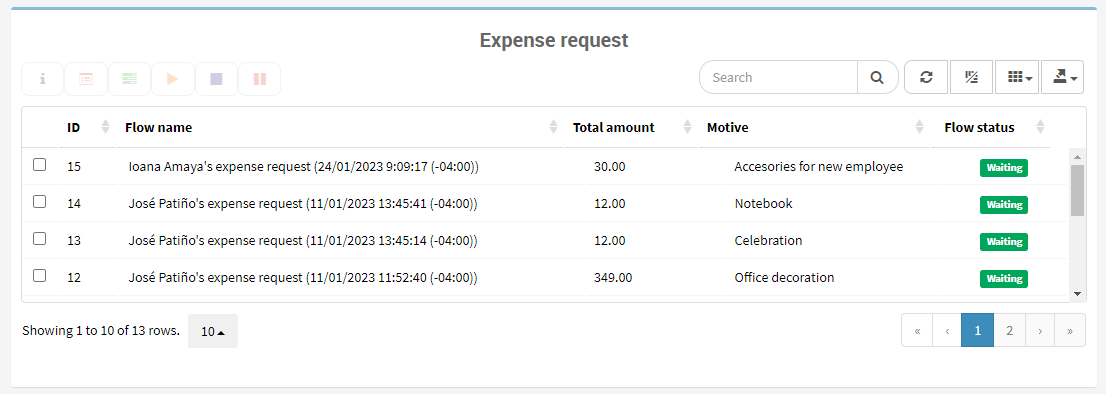
Fig. 65 Custom view example¶
Customized charts can be created in order to perform visual monitoring of your processes.
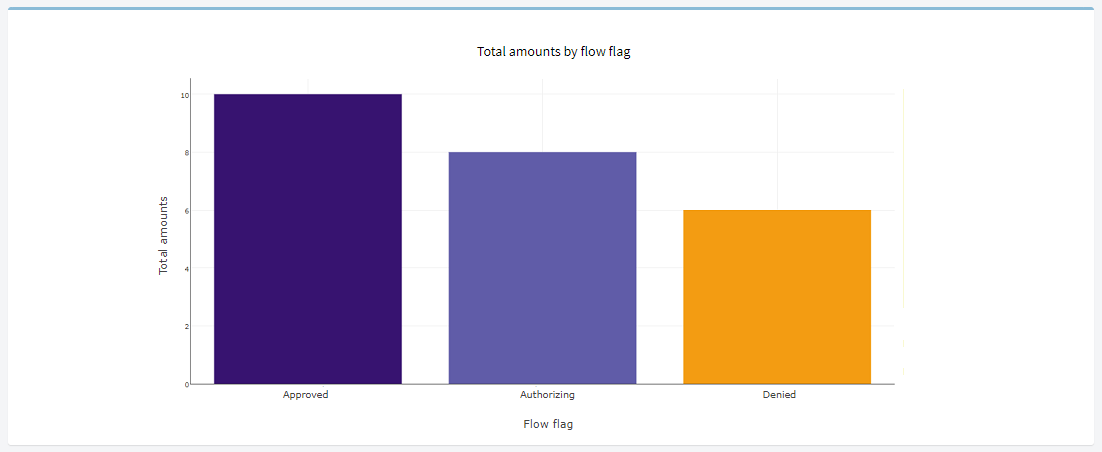
Fig. 66 Chart example¶
Within the dashboard, information is displayed in views, charts and KPIs allowing users to access all of the information at once.
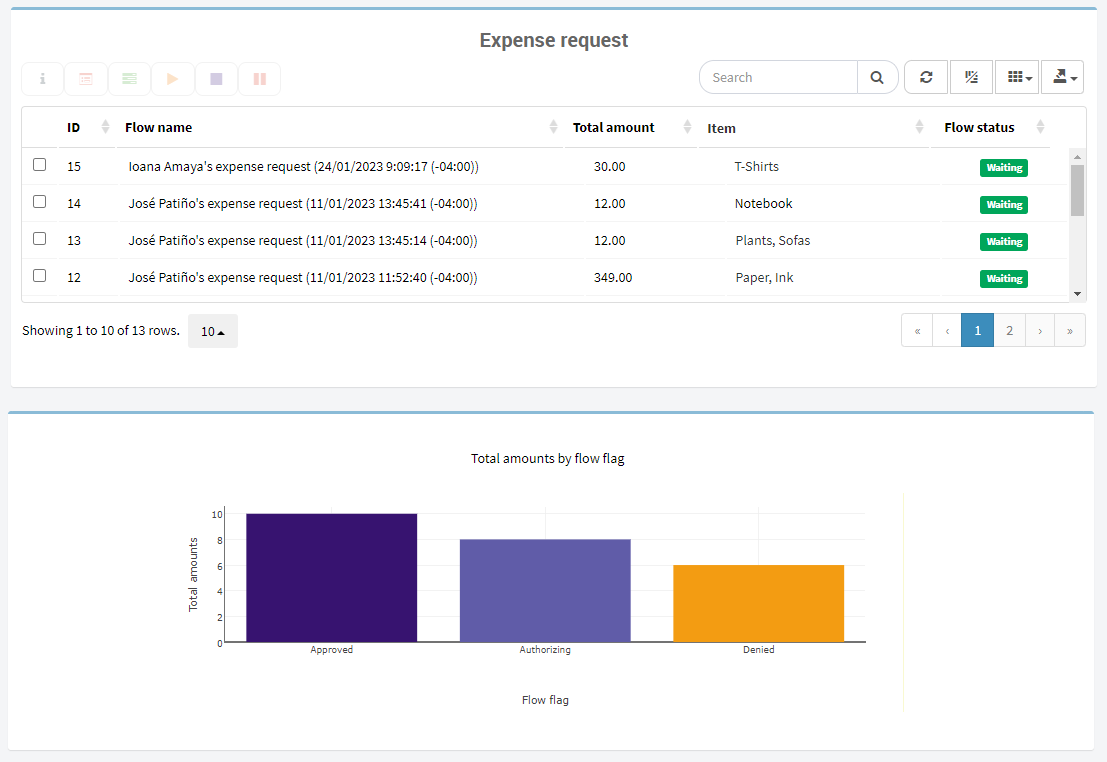
Fig. 67 Dashboard example¶
Qflow Team: organizational model and team manager¶
This tool can be used to represent each organization’s structure and its members, within the system. Additionally, user properties and their configuration can also be managed through this tool.
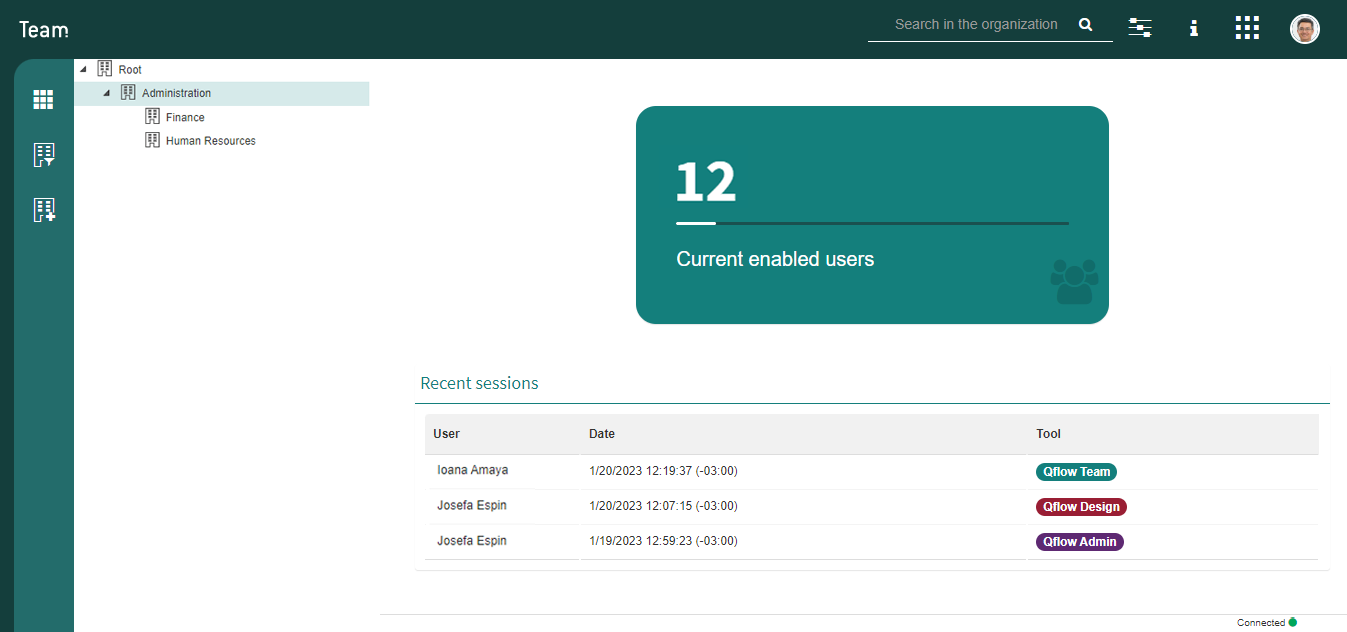
Fig. 68 Qflow Team¶
Organizational models manage three types of members: nodes, groups and users.
Nodes allow the model’s organizational structure to be organized hierarchically. A particular node represents the structure’s root. Additionally, a single node can contain both groups and users. It is possible to organize users similarly to the businesses’ real structures.
Groups allow the grouping of users who bear similar properties. As an example, it is possible to group users who have the same responsibilities. As well as grouping users, groups can contain other groups.
Users represent every Qflow user, and while they can be members of several groups, they cannot belong to more than one node.
Users and groups can be created within each node.
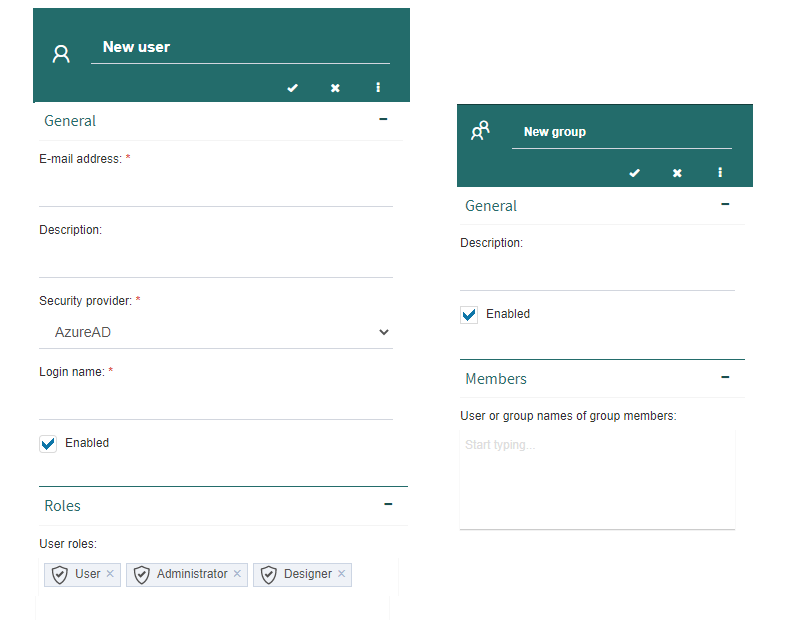
Fig. 69 User and group creation panels¶
Several configurations such as tool permissions, calendars, security roles, security providers, login reports and permits audits, can be managed from within Qflow Team.
The Calendars option allows the customization of calendars under which different users operate. As an example, this can be useful for organizations operating within various countries, since they operate under different calendars (holidays, work regime, etc.).
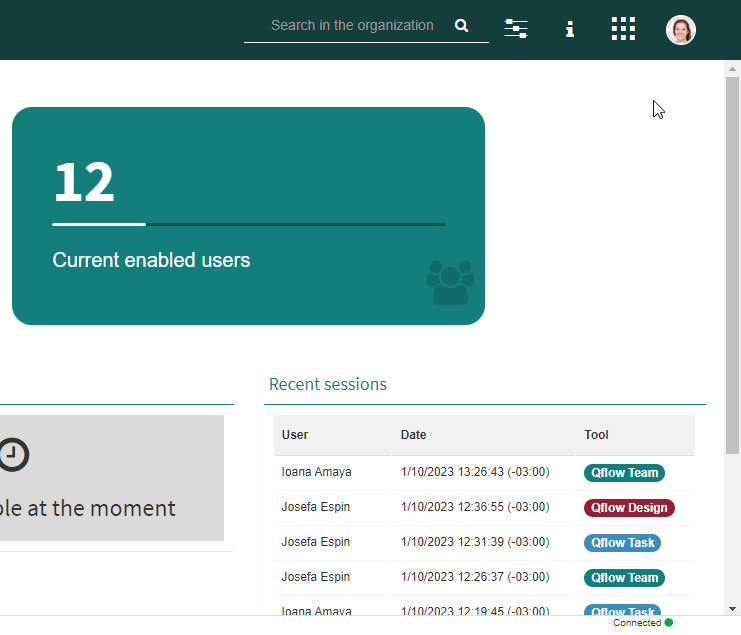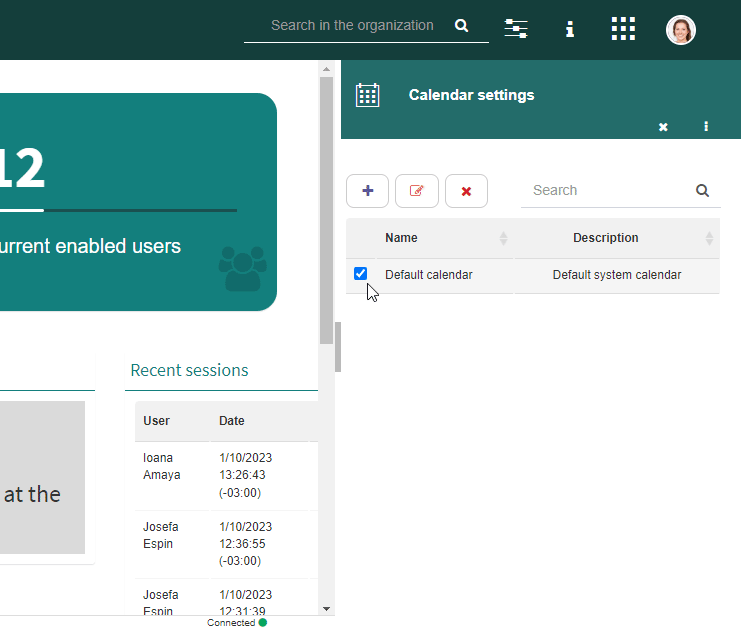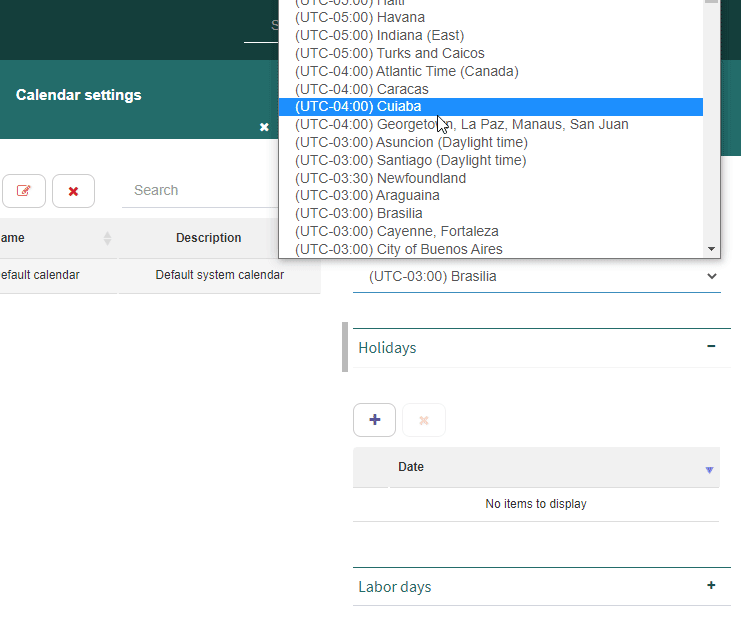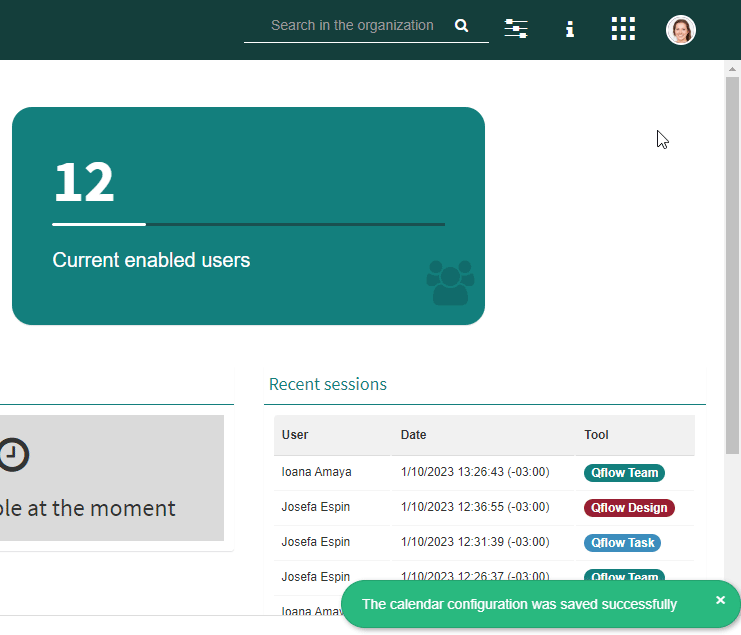
Fig. 70 Calendar configuration¶
The Login report option shows which users have successfully logged in into each Qflow tool in a determined time period. Additionally, logouts and failed logins are also displayed.
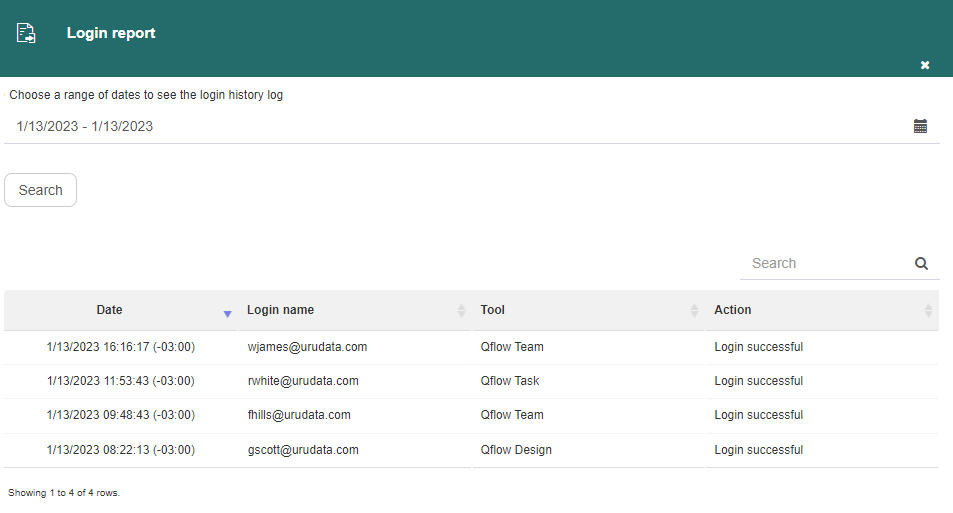
Fig. 71 Login report panel¶
Qflow Admin: system administration and monitoring¶
This tool manages settings in regard to the whole system and several elements which affect the overall performance, such as tools and services, extended properties, licenses, notification services, workspaces and system parameters.
Fig. 72 Qflow Admin¶
Within Services States, each service and Qflow tool can be monitored, in order to check their correct functioning.
Within Qflow Admin it is also possible to modify system parameters. These control various aspects of the products functioning. For instance, it is posible to manage sessions’ duration, as well as Google and Microsoft logins, etc.
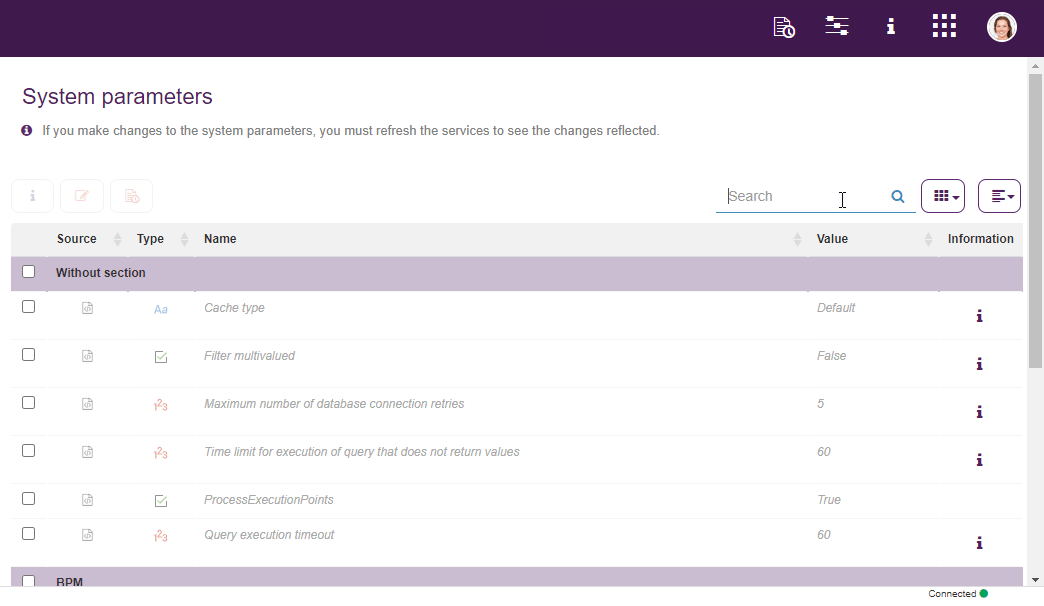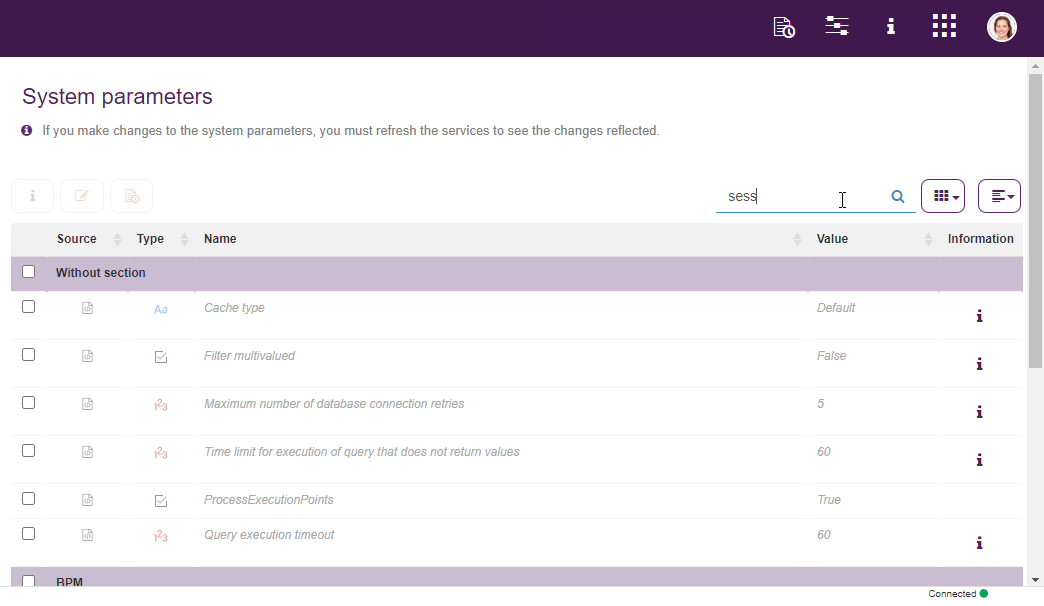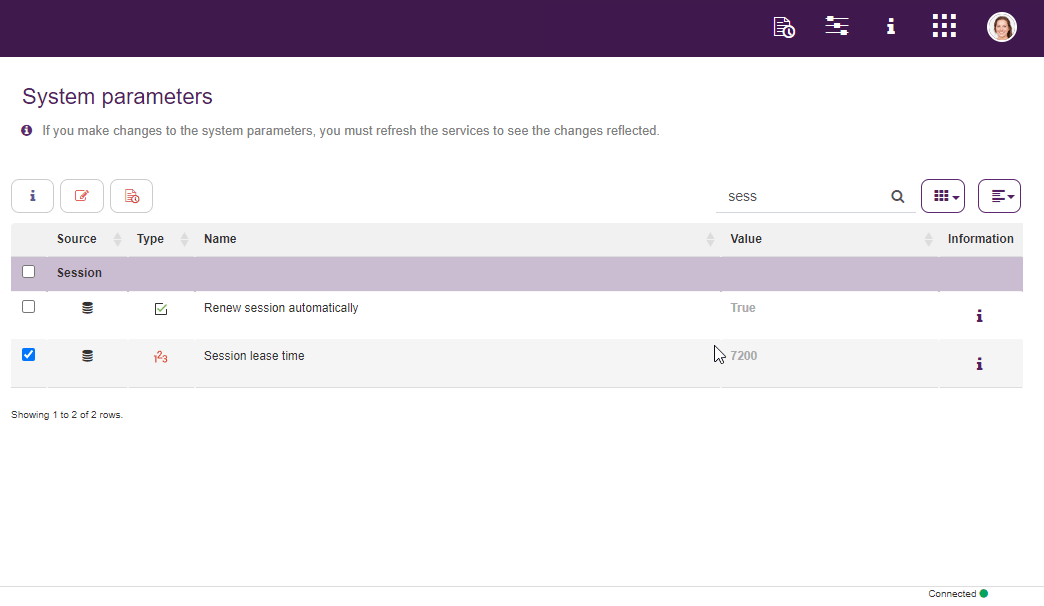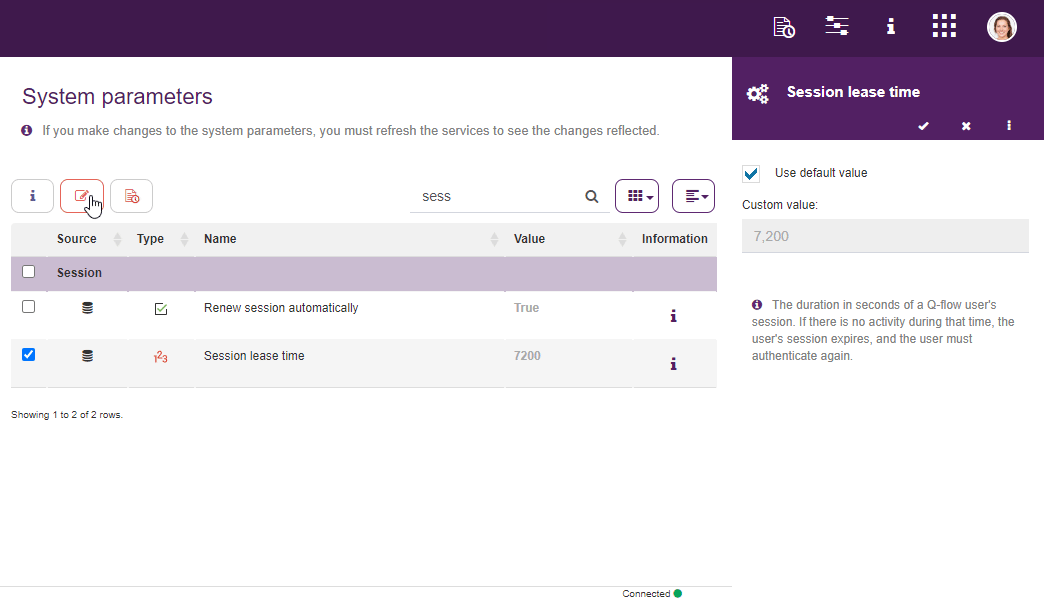
Fig. 73 System paremeters¶
Extended properties are defined by the orgnization. They can be seen in the properties panel of each organizational model member (user, group, node), within Qflow Team.
It is also posible to manage Qflow licenses, see which have expired and which haven’t, add new ones and check their respective consumption, etc.
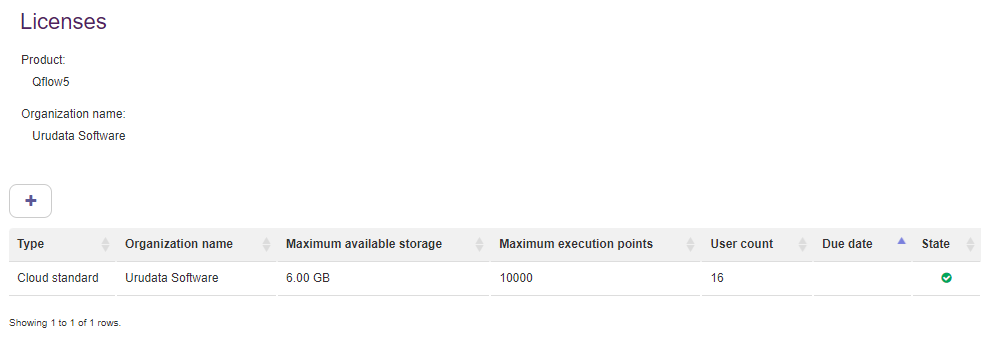
Fig. 74 Qflow licenses¶
Workspaces support multiple workspaces installation, or multi-tenancy. This adds an additional organizational layer to the system, through which a single server and database can hold different data, but share global settings. This system is comprised of a primary workspace (tenant) and a number of secondary workspaces, which can be managed from this section.
The notifier services section allows to visualize and manage services, either by adding, editing or removing them.
For further information of each of the tools, please refer to their respective manuals. There, you’ll find detailed documentation of both their functionalities and possible uses.
Qflow Task manual
Qflow Design manual
Qflow Team manual
Qflow Admin manual